Ang2-Targeted Combination Therapy for Cancer Treatment
- PMID: 35874764
- PMCID: PMC9305611
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.949553
Ang2-Targeted Combination Therapy for Cancer Treatment
Abstract
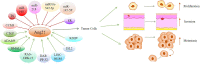
Angiopoietin-2 (Ang2), a member of the angiopoietin family, is widely involved in the process of vascular physiology, bone physiology, adipose tissue physiology and the occurrence and development of inflammation, cardiac hypertrophy, rheumatoid, tumor and other diseases under pathological conditions. Proliferation and metastasis of cancer largely depend on angiogenesis. Therefore, anti-angiogenesis has become the target of tumor therapy. Due to the Ang2 plays a key role in promoting angiogenesis and stability in vascular physiology, the imbalance of its expression is an important condition for the occurrence and development of cancer. It has been proved that blocking Ang2 can inhibit the growth, invasion and metastasis of cancer cells. In recent years, research has been constantly supplemented. We focus on the mechanisms that regulate the expression of Ang2 mRNA and protein levels in different cancers, contributing to a better understanding of how Ang2 exerts different effects in different cancers and stages, as well as facilitating more specific targeting of relevant molecules in cancer therapy. At the same time, the importance of Ang2 in cancer growth, metastasis, prognosis and combination therapy is pointed out. And finally, we will discuss the current investigations and future challenges of combining Ang2 inhibition with chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and radiotherapy to increase its efficacy in cancer patients. This review provides a theoretical reference for the development of new targets and effective combination therapy strategies for cancer treatment in the future.
Keywords: Ang2; Antiangiogenic therapy; Cancer development; Combination therapy; Targeting therapy.
Copyright © 2022 Liu, Liu, Fu, Wang, Tang, Isah, Chen and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- de Marinis F, Bria E, Ciardiello F, Crinò L, Douillard J, Griesinger F, et al. International Experts Panel Meeting of the Italian Association of Thoracic Oncology on Antiangiogenetic Drugs for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Realities and Hopes. J Thorac Oncol (2016) 11:1153–69. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2016.03.015 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

