Circ_0005918 Sponges miR-622 to Aggravate Intervertebral Disc Degeneration
- PMID: 35874804
- PMCID: PMC9304550
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2022.905213
Circ_0005918 Sponges miR-622 to Aggravate Intervertebral Disc Degeneration
Abstract
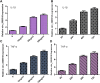
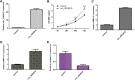
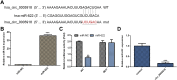
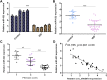
Intervertebral discdegeneration (IDD) is the most common cause of lower back pain, but the exact molecular mechanism of IDD is still unknown. Recently, studies have shown that circular RNAs (circRNAs) regulate diverse biological procedures such as cell metastasis, growth, metabolism, migration, apoptosis, and invasion. We demonstrated that IL-1β and TNF-α induced circ_0005918 expression in the NP cell, and circ_0005918 was overexpressed in the IDD group compared with the control group. Moreover, the upregulated expression of circ_0005918 was associated with disc degeneration degree. The elevated expression of circ_0005918 promoted cell growth and ECM degradation, and it induced secretion of inflammatory cytokines including IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α. Moreover, we found that circ_0005918 sponged miR-622 in the NP cell. In addition, the exposure to IL-1β and TNF-α suppressed the expression of miR-622, which was downregulated in the IDD group compared with the control group. Furthermore, the downregulated expression of miR-622 was associated with disc degeneration degree. The expression level of miR-622 was negatively associated with circ_0005918 expression in the IDD group. In conclusion, circ_0005918 regulated cell growth, ECM degradation, and secretion of inflammatory cytokines by regulating miR-622 expression. These data suggested that circ_0005918 played important roles in the development of IDD via sponging miR-622.
Keywords: cancers; circ_0005918; circular RNAs; intervertebral disc degeneration; miR-622.
Copyright © 2022 Cui, Zhao and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

