Somatic DNA Damage Response and Homologous Repair Gene Alterations and Its Association With Tumor Variant Burden in Breast Cancer Patients With Occupational Exposure to Pesticides
- PMID: 35875117
- PMCID: PMC9305859
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.904813
Somatic DNA Damage Response and Homologous Repair Gene Alterations and Its Association With Tumor Variant Burden in Breast Cancer Patients With Occupational Exposure to Pesticides
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Somatic DNA damage response and homologous repair gene alterations and its association with tumor variant burden in breast cancer patients with occupational exposure to pesticides.Front Oncol. 2022 Sep 23;12:1014392. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1014392. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36212417 Free PMC article.
Abstract
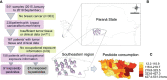
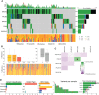
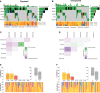
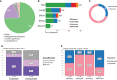
Homologous recombination is a crucial pathway that is specialized in repairing double-strand breaks; thus, alterations in genes of this pathway may lead to loss of genomic stability and cell growth suppression. Pesticide exposure potentially increases cancer risk through several mechanisms, such as the genotoxicity caused by chronic exposure, leading to gene alteration. To analyze this hypothesis, we investigated if breast cancer patients exposed to pesticides present a different mutational pattern in genes related to homologous recombination (BRCA1, BRCA2, PALB2, and RAD51D) and damage-response (TP53) concerning unexposed patients. We performed multiplex PCR-based assays and next-generation sequencing (NGS) of all coding regions and flanking splicing sites of BRCA1, BRCA2, PALB2, TP53, and RAD51D in 158 unpaired tumor samples from breast cancer patients on MiSeq (Illumina) platform. We found that exposed patients had tumors with more pathogenic and likely pathogenic variants than unexposed patients (p = 0.017). In general, tumors that harbored a pathogenic or likely pathogenic variant had a higher mutational burden (p < 0.001). We also observed that breast cancer patients exposed to pesticides had a higher mutational burden when diagnosed before 50 years old (p = 0.00978) and/or when carrying BRCA1 (p = 0.0138), BRCA2 (p = 0.0366), and/or PALB2 (p = 0.00058) variants, a result not found in the unexposed group. Our results show that pesticide exposure impacts the tumor mutational landscape and could be associated with the carcinogenesis process, therapy response, and disease progression. Further studies should increase the observation period in exposed patients to better evaluate the impact of these findings.
Keywords: breast cancer; mutational burden; occupational exposure; pesticides; somatic.
Copyright © 2022 Scandolara, Valle, Teixeira, Scherer, de Armas, Furtado, Boroni, Jaques, Alves, Rech, Panis and Bonvicino.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Friedrich K, Silveira da GR, Amazonas JC, Gurgel A do M, Almeida de VES, Sarpa M. Situação Regulatória Internacional De Agrotóxicos Com Uso Autorizado No Brasil: Potencial De Danos Sobre a Saúde E Impactos Ambientais. Cad Saude Publica (2021) 37(4):e00061820. doi: 10.1590/0102-311x00061820 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

