CT-Based Radiomics Nomogram Improves Risk Stratification and Prediction of Early Recurrence in Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Partial Hepatectomy
- PMID: 35875140
- PMCID: PMC9302642
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.896002
CT-Based Radiomics Nomogram Improves Risk Stratification and Prediction of Early Recurrence in Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Partial Hepatectomy
Abstract
Objectives: To develop and validate an intuitive computed tomography (CT)-based radiomics nomogram for the prediction and risk stratification of early recurrence (ER) in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients after partial hepatectomy.
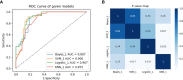
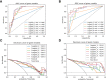
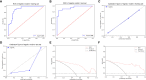
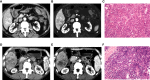
Methods: A total of 132 HCC patients treated with partial hepatectomy were retrospectively enrolled and assigned to training and test sets. Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator and gradient boosting decision tree were used to extract quantitative radiomics features from preoperative contrast-enhanced CT images of the HCC patients. The radiomics features with predictive value for ER were used, either alone or in combination with other predictive features, to construct predictive models. The best performing model was then selected to develop an intuitive, simple-to-use nomogram, and its performance in the prediction and risk stratification of ER was evaluated using the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC), calibration curve, and decision curve analysis (DCA).
Results: The radiomics model based on the radiomics score (Rad-score) achieved AUCs of 0.870 and 0.890 in the training and test sets, respectively. Among the six predictive models, the combined model based on the Rad-score, Edmondson grade, and tumor size had the highest AUCs of 0.907 in the training set and 0.948 in the test set and was used to develop an intuitive nomogram. Notably, the calibration curve and DCA for the nomogram showed good calibration and clinical application. Moreover, the risk of ER was significantly different between the high- and low-risk groups stratified by the nomogram (p <0.001).
Conclusions: The CT-based radiomics nomogram developed in this study exhibits outstanding performance for ER prediction and risk stratification. As such, this intuitive nomogram holds promise as a more effective and user-friendly tool in predicting ER for HCC patients after partial hepatectomy.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma; machine learning; models; nomograms; radiomics; recurrence.
Copyright © 2022 Wu, Yu, Zhang, Zhu, Chen and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The reviewer ZD declared a shared parent affiliation with the authors to the handling editor at the time of review.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Radiomics for preoperative prediction of early recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2023 Jun 7;13:1114983. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1114983. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37350952 Free PMC article.
-
18F-FDG PET/CT-based radiomics nomogram for preoperative prediction of macrotrabecular-massive hepatocellular carcinoma: a two-center study.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2023 Feb;48(2):532-542. doi: 10.1007/s00261-022-03722-y. Epub 2022 Nov 12. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2023. PMID: 36370179
-
Radiomics nomogram based on multi-parametric magnetic resonance imaging for predicting early recurrence in small hepatocellular carcinoma after radiofrequency ablation.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 10;12:1013770. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1013770. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36439458 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative contrast-enhanced computed tomography-based radiomics model for overall survival prediction in hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2022 Aug 21;28(31):4376-4389. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i31.4376. World J Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 36159012 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Prediction power of radiomics in early recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Jul 5;103(27):e38721. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000038721. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38968499 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Prediction of early recurrence of HCC after hepatectomy by contrast-enhanced ultrasound-based deep learning radiomics.Front Oncol. 2022 Sep 28;12:930458. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.930458. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36248986 Free PMC article.
-
Role of radiomics as a predictor of disease recurrence in ovarian cancer: a systematic review.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2024 Oct;49(10):3540-3547. doi: 10.1007/s00261-024-04330-8. Epub 2024 May 15. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2024. PMID: 38744703 Free PMC article.
-
Gut microbiome as a biomarker for predicting early recurrence of HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Sci. 2023 Dec;114(12):4717-4731. doi: 10.1111/cas.15983. Epub 2023 Oct 1. Cancer Sci. 2023. PMID: 37778742 Free PMC article.
-
Radiomics for preoperative prediction of early recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2023 Jun 7;13:1114983. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1114983. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37350952 Free PMC article.
-
From detection to elimination: iron-based nanomaterials driving tumor imaging and advanced therapies.Front Oncol. 2025 Feb 7;15:1536779. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1536779. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39990682 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

