Flow test by the International Dysphagia Diet Standardization Initiative reveals distinct viscosity parameters of three thickening agents
- PMID: 35875213
- PMCID: PMC9304459
- DOI: 10.1007/s13197-022-05369-5
Flow test by the International Dysphagia Diet Standardization Initiative reveals distinct viscosity parameters of three thickening agents
Abstract
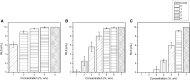
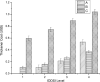
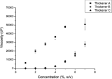
The International Dysphagia Diet Standardization Initiative (IDDSI) flow test is useful for the global standardization of food consistencies of dysphagia patients. In clinical practice, different compositions of food thickeners are commonly used, directly influencing viscosity parameters and swallowing physiology. We aimed to compare the IDDSI thickness levels, remaining volume in the syringe (RVS), and viscosity parameters of three different food thickeners. As a secondary objective, we compared the cost of preparing 100 mL of thickened drinks using the studied thickeners. Thickeners A (xanthan gum), B (corn starch, tara gum, xanthan gum, and guar gum), and C (corn starch) were prepared in increasing concentrations from 1 to 7 g/100 mL and were assayed in quintuplicate using the IDDSI flow test. Thickeners A, B, and C presented statistically different results for the IDDSI levels, RVS, and viscosity parameters at all concentrations. Thickener A reached higher levels in the IDDSI framework, RVS, and viscosity parameters compared with thickeners B and C. A large range of RVS was observed at different concentrations for thickener B compared with C. Regarding viscosity, thickeners B and C, with corn starch in their composition, showed exponential behavior as concentrations increased, while thickener A presented a linear trend. The thickener composition was significantly influenced by IDDSI classification, RVS, and viscosity parameters. The study shows that xanthan gum thickeners present less variability in IDDSI, RVS, and viscosity compared with starch-based thickeners.
Keywords: Deglutition disorders; Thickened liquid; Thickening agent; Viscosity.
© Association of Food Scientists & Technologists (India) 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they do not have any conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative study of IDDSI flow test and line-spread test of thickened water prepared with different dysphagia thickeners.J Texture Stud. 2018 Dec;49(6):653-658. doi: 10.1111/jtxs.12360. Epub 2018 Sep 21. J Texture Stud. 2018. PMID: 30187484
-
Relationship between International Dysphagia Diet Standardisation Initiative Flow Test and Consistometric Measures for Consistency Classification: An Examination of Thickened Liquids Prepared Using Starch-Based and Xanthan Gum-Based Thickening Agents.Folia Phoniatr Logop. 2025;77(2):161-169. doi: 10.1159/000540118. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Folia Phoniatr Logop. 2025. PMID: 39043153 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of National Dysphagia Diet and International Dysphasia Diet Standardization Initiative Levels for Thickened Drinks Prepared with a Commercial Xanthan Gum-Based Thickener Used for Patients with Dysphagia.Prev Nutr Food Sci. 2023 Mar 31;28(1):83-88. doi: 10.3746/pnf.2023.28.1.83. Prev Nutr Food Sci. 2023. PMID: 37066029 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of thickening agents on rheological properties and sensory attributes of dysphagic diet.J Texture Stud. 2021 Dec;52(5-6):587-602. doi: 10.1111/jtxs.12596. Epub 2021 Apr 7. J Texture Stud. 2021. PMID: 33760237 Review.
-
Clinical Aspects of Thickeners for Pediatric Gastroesophageal Reflux and Oropharyngeal Dysphagia.Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2019 May 16;21(7):30. doi: 10.1007/s11894-019-0697-2. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2019. PMID: 31098722 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of Beverage Viscosity Based on the International Dysphagia Diet Standardisation Initiative and Its Correspondence to the Japanese Dysphagia Diet 2021.Nutrients. 2025 Mar 17;17(6):1051. doi: 10.3390/nu17061051. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40292446 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of temperature variation on the levels of the International Dysphagia Diet Standardization Initiative.Codas. 2024 Sep 13;36(6):e20230315. doi: 10.1590/2317-1782/20242023315pt. eCollection 2024. Codas. 2024. PMID: 39292109 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cichero JAY, Lam P, Steele CM, Hanson B, Chen J, Dantas RO, Duivestein J, Kayashita J, Lecko C, Murray J, Pillay M, Riquelme L, Stanschus S. Development of international terminology and definitions for texture-modified foods and thickened fluids used in dysphagia management: the IDDSI framework. Dysphagia. 2017;32(2):293–314. doi: 10.1007/s00455-016-9758-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
