Mesial Temporal Lobe Epilepsy (MTLE) Drug-Refractoriness Is Associated With P2X7 Receptors Overexpression in the Human Hippocampus and Temporal Neocortex and May Be Predicted by Low Circulating Levels of miR-22
- PMID: 35875355
- PMCID: PMC9300956
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2022.910662
Mesial Temporal Lobe Epilepsy (MTLE) Drug-Refractoriness Is Associated With P2X7 Receptors Overexpression in the Human Hippocampus and Temporal Neocortex and May Be Predicted by Low Circulating Levels of miR-22
Abstract
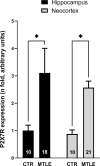
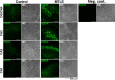
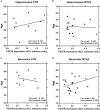
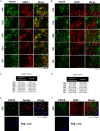
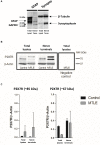
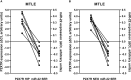
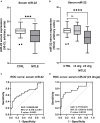
Objective: ATP-gated ionotropic P2X7 receptors (P2X7R) actively participate in epilepsy and other neurological disorders. Neocortical nerve terminals of patients with Mesial Temporal Lobe Epilepsy with Hippocampal Sclerosis (MTLE-HS) express higher P2X7R amounts. Overexpression of P2X7R bolsters ATP signals during seizures resulting in glial cell activation, cytokines production, and GABAergic rundown with unrestrained glutamatergic excitation. In a mouse model of status epilepticus, increased expression of P2X7R has been associated with the down-modulation of the non-coding micro RNA, miR-22. MiR levels are stable in biological fluids and normally reflect remote tissue production making them ideal disease biomarkers. Here, we compared P2X7R and miR-22 expression in epileptic brains and in the serum of patients with MTLE-HS, respectively. Methods: Quantitative RT-PCR was used to evaluate the expression of P2X7R in the hippocampus and anterior temporal lobe of 23 patients with MTLE-HS and 10 cadaveric controls. Confocal microscopy and Western blot analysis were performed to assess P2X7R protein amounts. MiR-22 expression was evaluated in cell-free sera of 40 MTLE-HS patients and 48 healthy controls. Results: Nerve terminals of the hippocampus and neocortical temporal lobe of MTLE-HS patients overexpress (p < 0.05) an 85 kDa P2X7R protein whereas the normally occurring 67 kDa receptor protein dominates in the brain of the cadaveric controls. Contrariwise, miR-22 serum levels are diminished (p < 0.001) in MTLE-HS patients compared to age-matched control blood donors, a situation that is more evident in patients requiring multiple (>3) anti-epileptic drug (AED) regimens. Conclusion: Data show that there is an inverse relationship between miR-22 serum levels and P2X7R expression in the hippocampus and neocortex of MTLE-HS patients, which implies that measuring serum miR-22 may be a clinical surrogate of P2X7R brain expression in the MTLE-HS. Moreover, the high area under the ROC curve (0.777; 95% CI 0.629-0.925; p = 0.001) suggests that low miR-22 serum levels may be a sensitive predictor of poor response to AEDs among MTLE-HS patients. Results also anticipate that targeting the miR-22/P2X7R axis may be a good strategy to develop newer AEDs.
Keywords: P2X7 purinoceptor; hippocampus; mesotemporal lobe epilepsy; miR-22; microRNAs; refractory epilepsy.
Copyright © 2022 Guerra Leal, Barros-Barbosa, Ferreirinha, Chaves, Rangel, Santos, Carvalho, Martins-Ferreira, Samões, Freitas, Lopes, Ramalheira, Lobo, Martins da Silva, Costa and Correia-de-Sá.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Up-regulation of P2X7 receptor-mediated inhibition of GABA uptake by nerve terminals of the human epileptic neocortex.Epilepsia. 2016 Jan;57(1):99-110. doi: 10.1111/epi.13263. Epub 2015 Dec 30. Epilepsia. 2016. PMID: 26714441
-
MicroRNAs miR-629-3p, miR-1202 and miR-1225-5p as potential diagnostic and surgery outcome biomarkers for mesial temporal lobe epilepsy with hippocampal sclerosis.Neurochirurgie. 2022 Dec;68(6):583-588. doi: 10.1016/j.neuchi.2022.06.002. Epub 2022 Jun 11. Neurochirurgie. 2022. PMID: 35700789
-
MicroRNA and mesial temporal lobe epilepsy with hippocampal sclerosis: Whole miRNome profiling of human hippocampus.Epilepsia. 2017 Oct;58(10):1782-1793. doi: 10.1111/epi.13870. Epub 2017 Aug 16. Epilepsia. 2017. PMID: 28815576
-
Understanding the association of neurocysticercosis and mesial temporal lobe epilepsy and its impact on the surgical treatment of patients with drug-resistant epilepsy.Epilepsy Behav. 2017 Nov;76:168-177. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2017.02.030. Epub 2017 Apr 24. Epilepsy Behav. 2017. PMID: 28462844 Review.
-
Meta-analysis of voxel-based morphometry studies of gray matter abnormalities in patients with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy and unilateral hippocampal sclerosis.Brain Imaging Behav. 2018 Oct;12(5):1497-1503. doi: 10.1007/s11682-017-9797-5. Brain Imaging Behav. 2018. PMID: 29302917
Cited by
-
Pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of epilepsy: electromagnetic stimulation-mediated neuromodulation therapy and new technologies.Neural Regen Res. 2025 Apr 1;20(4):917-935. doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-23-01444. Epub 2024 Apr 3. Neural Regen Res. 2025. PMID: 38989927 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating miRNAs as Novel Clinical Biomarkers in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy.Noncoding RNA. 2024 Mar 17;10(2):18. doi: 10.3390/ncrna10020018. Noncoding RNA. 2024. PMID: 38525737 Free PMC article. Review.
-
microRNA profilings identify plasma biomarkers and targets associated with pediatric epilepsy patients.Pediatr Res. 2024 Mar;95(4):996-1008. doi: 10.1038/s41390-023-02864-z. Epub 2023 Oct 27. Pediatr Res. 2024. PMID: 37884644 Free PMC article.
-
The P2X7 Receptor as a Mechanistic Biomarker for Epilepsy.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 12;24(6):5410. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065410. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36982485 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of microRNAs in neurobiology and pathophysiology of the hippocampus.Front Mol Neurosci. 2023 Sep 4;16:1226413. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2023.1226413. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37727513 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Almeida Silva L. F., Reschke C. R., Nguyen N. T., Langa E., Sanz-Rodriguez A., Gerbatin R. R., et al. . (2020). Genetic deletion of microRNA-22 blunts the inflammatory transcriptional response to status epilepticus and exacerbates epilepsy in mice. Mol. Brain 13:114. 10.1186/s13041-020-00653-x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Amorim R. P., Araujo M. G. L., Valero J., Lopes-Cendes I., Pascoal V. D. B., Malva J. O., et al. . (2017). Silencing of P2X7R by RNA interference in the hippocampus can attenuate morphological and behavioral impact of pilocarpine-induced epilepsy. Purinergic Signal. 13, 467–478. 10.1007/s11302-017-9573-4 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

