Novel Photo- and Thermo-Responsive Nanocomposite Hydrogels Based on Functionalized rGO and Modified SIS/Chitosan Polymers for Localized Treatment of Malignant Cutaneous Melanoma
- PMID: 35875496
- PMCID: PMC9300866
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.947616
Novel Photo- and Thermo-Responsive Nanocomposite Hydrogels Based on Functionalized rGO and Modified SIS/Chitosan Polymers for Localized Treatment of Malignant Cutaneous Melanoma
Abstract
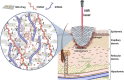
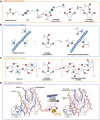
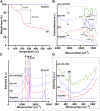
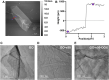
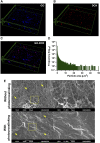
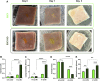
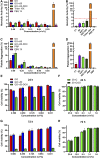
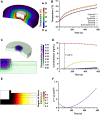
Melanoma is an aggressive type of skin cancer that accounts for over 75% of skin cancer deaths despite comprising less than 5% of all skin cancers. Despite promising improvements in surgical approaches for melanoma resection, the survival of undetectable microtumor residues has remained a concern. As a result, hyperthermia- and drug-based therapies have grown as attractive techniques to target and treat cancer. In this work, we aim to develop a stimuli-responsive hydrogel based on chitosan methacrylate (ChiMA), porcine small intestine submucosa methacrylate (SISMA), and doxorubicin-functionalized reduced graphene oxide (rGO-DOX) that eliminates microtumor residues from surgically resected melanoma through the coupled effect of NIR light-induced photothermal therapy and heat-induced doxorubicin release. Furthermore, we developed an in silico model to optimize heat and mass transport and evaluate the proposed chemo/photothermal therapy in vitro over melanoma cell cultures.
Keywords: COMSOL multiphysics; melanoma; methacrylation; photothermal therapy; reduced graphene oxide.
Copyright © 2022 Céspedes-Valenzuela, Sánchez-Rentería, Cifuentes, Gómez, Serna, Rueda-Gensini, Ostos, Muñoz-Camargo and Cruz.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Reduced graphene oxide (rGO) hybridized hydrogel as a near-infrared (NIR)/pH dual-responsive platform for combined chemo-photothermal therapy.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2019 Feb 15;536:160-170. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2018.10.050. Epub 2018 Oct 19. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2019. PMID: 30366181
-
Injectable in situ forming thermo-responsive graphene based hydrogels for cancer chemo-photothermal therapy and NIR light-enhanced antibacterial applications.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020 Dec;117:111294. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2020.111294. Epub 2020 Jul 24. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020. PMID: 32919655
-
Dynamic-Covalent Hydrogel with NIR-Triggered Drug Delivery for Localized Chemo-Photothermal Combination Therapy.Biomacromolecules. 2020 Feb 10;21(2):556-565. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.9b01290. Epub 2019 Dec 12. Biomacromolecules. 2020. PMID: 31804804
-
The polyvinylpyrrolidone functionalized rGO/Bi2S3 nanocomposite as a near-infrared light-responsive nanovehicle for chemo-photothermal therapy of cancer.Nanoscale. 2016 Jun 2;8(22):11531-42. doi: 10.1039/c6nr01543c. Nanoscale. 2016. PMID: 27203525
-
Thermo-Responsive Hydrogels Coupled with Photothermal Agents for Biomedical Applications.Macromol Biosci. 2023 Dec;23(12):e2300214. doi: 10.1002/mabi.202300214. Epub 2023 Aug 17. Macromol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37526220 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel Photothermal Graphene-Based Hydrogels in Biomedical Applications.Polymers (Basel). 2024 Apr 15;16(8):1098. doi: 10.3390/polym16081098. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38675017 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advanced functionalized chitosan nanocomposites for hyperthermia-based cancer therapy.Med Oncol. 2025 May 12;42(6):208. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02768-4. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40353916 Review.
-
Advances in NIR-Responsive Natural Macromolecular Hydrogel Assembly Drugs for Cancer Treatment.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Dec 4;15(12):2729. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15122729. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 38140070 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Graphene-Based Nanomaterials for Photothermal Therapy in Cancer Treatment.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Sep 6;15(9):2286. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15092286. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37765255 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ani C. J., Danyuo Y., Odusanya O. S., Soboyejo W. O. (2018). Computational Modeling of Drug Diffusion and Inductive Heating in an Implantable Biomedical Device for Localized Thermo-Chemotherapy of Cancer Cells/tissue. Cogent Eng. 5, 1463814. 10.1080/23311916.2018.1463814 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

