Corynebacterium matruchotii: A Confirmed Calcifying Bacterium With a Potentially Important Role in the Supragingival Plaque
- PMID: 35875585
- PMCID: PMC9298747
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.940643
Corynebacterium matruchotii: A Confirmed Calcifying Bacterium With a Potentially Important Role in the Supragingival Plaque
Abstract
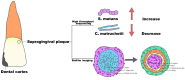
Corynebacterium matruchotii is a reported calcifying bacterium that can usually be isolated from dental calculus and induce mineralization in vitro. In recent years, based on in situ hybridization probe and sequencing technology, researchers have discovered the central "pillar" role of C. matruchotii in supragingival plaque, and many studies focused on bacterial interactions in the biofilm structure dominated by C. matruchotii have been conducted. Besides, C. matruchotii seems to be an indicator of "caries-free" oral status according to imaging and sequencing studies. Therefore, in this review, we summarize C. matruchotii 's role in supragingival plaque based on the structure, interactions, and potential connections with oral diseases.
Keywords: Corynebacterium matruchotii; bacterial interaction; biofilm structure; oral diseases; supragingival plaque.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Zhou, Su, Li and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Corynebacterium matruchotii Demography and Adhesion Determinants in the Oral Cavity of Healthy Individuals.Microorganisms. 2020 Nov 13;8(11):1780. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8111780. Microorganisms. 2020. PMID: 33202844 Free PMC article.
-
Dental plaque microbiota profiles of children with caries-free and caries-active dentition.J Dent. 2021 Jan;104:103539. doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2020.103539. Epub 2020 Nov 25. J Dent. 2021. PMID: 33248211
-
Diversity within reference strains of Corynebacterium matruchotii includes Corynebacterium durum and a novel organism.J Clin Microbiol. 2001 Mar;39(3):943-8. doi: 10.1128/JCM.39.3.943-948.2001. J Clin Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11230408 Free PMC article.
-
Dental calculus: recent insights into occurrence, formation, prevention, removal and oral health effects of supragingival and subgingival deposits.Eur J Oral Sci. 1997 Oct;105(5 Pt 2):508-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1997.tb00238.x. Eur J Oral Sci. 1997. PMID: 9395117 Review.
-
Spatial scale in analysis of the dental plaque microbiome.Periodontol 2000. 2021 Jun;86(1):97-112. doi: 10.1111/prd.12364. Epub 2021 Mar 10. Periodontol 2000. 2021. PMID: 33690940 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Integrated multi-omics analysis reveals the functional signature of microbes and metabolomics in pre-diabetes individuals.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 Jul;13(7):e0145924. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01459-24. Epub 2025 Jun 9. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 40488467 Free PMC article.
-
Human oral mucosa and oral microbiome interactions following supragingival plaque reconstitution in healthy volunteers: a diet-controlled balanced design proof-of-concept model to investigate oral pathologies.J Oral Microbiol. 2023 Aug 22;15(1):2246279. doi: 10.1080/20002297.2023.2246279. eCollection 2023. J Oral Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37621744 Free PMC article.
-
Heterogeneous lineage-specific arginine deiminase expression within dental microbiome species.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Apr 2;12(4):e0144523. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01445-23. Epub 2024 Feb 27. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38411054 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal Microbiome Changes in Supragingival Biofilm Transcriptomes Induced by Orthodontics.JDR Clin Trans Res. 2024 Jul;9(3):265-276. doi: 10.1177/23800844231199393. Epub 2023 Oct 24. JDR Clin Trans Res. 2024. PMID: 37876206 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al-Hebshi N. N., Baraniya D., Chen T., Hill J., Puri S., Tellez M., et al. . (2019). Metagenome sequencing-based strain-level and functional characterization of supragingival microbiome associated with dental caries in children. J. Oral Microbiol. 11, 1557986. 10.1080/20002297.2018.1557986 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources