Unsymmetrical aromatic disulfides as SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitors: Molecular docking, molecular dynamics, and ADME scoring investigations
- PMID: 35875823
- PMCID: PMC9296233
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102226
Unsymmetrical aromatic disulfides as SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitors: Molecular docking, molecular dynamics, and ADME scoring investigations
Abstract
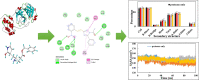
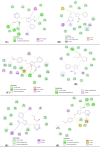
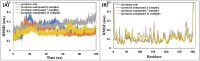
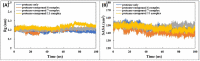
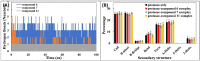
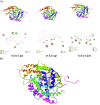
COVID-19 pandemic caused by very severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) agent is an ongoing major global health concern. The disease has caused more than 452 million affected cases and more than 6 million death worldwide. Hence, there is an urgency to search for possible medications and drug treatments. There are no approved drugs available to treat COVID-19 yet, although several vaccine candidates are already available and some of them are listed for emergency use by the world health organization (WHO). Identifying a potential drug candidate may make a significant contribution to control the expansion of COVID-19. The in vitro biological activity of asymmetric disulfides against coronavirus through the inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro) protein was reported. Due to the lack of convincing evidence those asymmetric disulfides have favorable pharmacological properties for the clinical treatment of Coronavirus, in silico evaluation should be performed to assess the potential of these compounds to inhibit the SARS-CoV-2 Mpro. In this context, we report herein the molecular docking for a series of 40 unsymmetrical aromatic disulfides as SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor. The optimal binding features of disulfides within the binding pocket of SARS-CoV-2 endoribonuclease protein (Protein Data Bank [PDB]: 6LU7) was described. Studied compounds were ranked for potential effectiveness, and those have shown high molecular docking scores were proposed as novel drug candidates against SARS-CoV-2. Moreover, the outcomes of drug similarity and ADME (Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion) analyses have may have the effectiveness of acting as medicines, and would be of interest as promising starting point for designing compounds against SARS-CoV-2. Finally, the stability of these three compounds in the complex with Mpro was validated through molecular dynamics (MD) simulation, in which they displayed stable trajectory and molecular properties with a consistent interaction profile.
Keywords: COVID-19; COVID-19, coronavirus disease 2019; CYP, cytochrome P450; Disulfides; HBA, hydrogen bond acceptor; HBD, hydrogen bond donor; MD, molecular dynamics; Main protease; Molecular docking; Molecular dynamics; Mpro, Main protease; PDB, Protein Data Bank; PSA, polar surface area; RB, rotatable bond count; RMSD, root-mean-square deviation; RMSF, root-mean-square fluctuation; Rg, radius of gyration; SARS-CoV-2; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2; SASA, solvent-accessible surface area; SMILES, simplified molecular input line entry system; WHO, World Health Organization.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Anand K., Ziebuhr J., Wadhwani P., Mesters J.R., Hilgenfeld R. Coronavirus main proteinase (3CLpro) structure: basis for design of anti-SARS drugs. Science. 2003;300(5626):1763–1767. - PubMed
-
- Aouidate A., Ghaleb A., Chtita S., Aarjane M., Ousaa A., Maghat M., Sbai A., Choukrad M., Bouachrine M., Lakhlifi T. Identification of a novel dual-target scaffold for 3CLpro and RdRp proteins of SARS-CoV-2 using 3D-similarity search, molecular docking, molecular dynamics and ADMET evaluation. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2020 doi: 10.1080/07391102.2020.1779130. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chtita S., Belhassan A., Bakhouch M., Taourati A.I., Aouidate A., Belaidi S., Moutaabbid M., Belaaouad S., Bouachrine M., Lakhlifi T. QSAR study of unsymmetrical aromatic Disulfides as potent avian SARS-CoV main protease inhibitors using quantum chemical descriptors and statistical methods. Chemomet. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2021;210(15) doi: 10.1016/j.chemolab.2021.104266. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
