Predicting patient experience of Invisalign treatment: An analysis using artificial neural network
- PMID: 35875850
- PMCID: PMC9314214
- DOI: 10.4041/kjod21.255
Predicting patient experience of Invisalign treatment: An analysis using artificial neural network
Abstract
Objective: Poor experience with Invisalign treatment affects patient compliance and, thus, treatment outcome. Knowing the potential discomfort level in advance can help orthodontists better prepare the patient to overcome the difficult stage. This study aimed to construct artificial neural networks (ANNs) to predict patient experience in the early stages of Invisalign treatment.
Methods: In total, 196 patients were enrolled. Data collection included questionnaires on pain, anxiety, and quality of life (QoL). A four-layer fully connected multilayer perception with three backpropagations was constructed to predict patient experience of the treatment. The input data comprised 17 clinical features. The partial derivative method was used to calculate the relative contributions of each input in the ANNs.
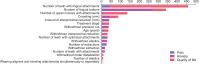
Results: The predictive success rates for pain, anxiety, and QoL were 87.7%, 93.4%, and 92.4%, respectively. ANNs for predicting pain, anxiety, and QoL yielded areas under the curve of 0.963, 0.992, and 0.982, respectively. The number of teeth with lingual attachments was the most important factor affecting the outcome of negative experience, followed by the number of lingual buttons and upper incisors with attachments.
Conclusions: The constructed ANNs in this preliminary study show good accuracy in predicting patient experience (i.e., pain, anxiety, and QoL) of Invisalign treatment. Artificial intelligence system developed for predicting patient comfort has potential for clinical application to enhance patient compliance.
Keywords: Aligners; Compliance; Computer algorithm; Pain.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Motivation, acceptance and problems of invisalign patients.J Orofac Orthop. 2005 Mar;66(2):162-73. doi: 10.1007/s00056-005-0429-0. J Orofac Orthop. 2005. PMID: 15827703 Clinical Trial. English, German.
-
[Establishment of artificial neural network model for predicting lymph node metastasis in patients with stage Ⅱ-Ⅲ gastric cancer].Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2022 Apr 25;25(4):327-335. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn441530-20220105-00010. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35461201 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Scanning electron microscopy evaluation of aligner fit on teeth.Angle Orthod. 2018 Sep;88(5):596-601. doi: 10.2319/120417-827.1. Epub 2018 Jun 18. Angle Orthod. 2018. PMID: 29911907 Free PMC article.
-
Basic concepts of artificial neural network (ANN) modeling and its application in pharmaceutical research.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2000 Jun;22(5):717-27. doi: 10.1016/s0731-7085(99)00272-1. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2000. PMID: 10815714 Review.
-
Applying artificial neural networks (ANNs) to solve solid waste-related issues: A critical review.Waste Manag. 2021 Apr 1;124:385-402. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2021.02.029. Epub 2021 Mar 2. Waste Manag. 2021. PMID: 33662770 Review.
Cited by
-
The Future of Orthodontics: Deep Learning Technologies.Cureus. 2024 Jun 10;16(6):e62045. doi: 10.7759/cureus.62045. eCollection 2024 Jun. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38989357 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of Artificial Intelligence in Orthodontics: Current State and Future Perspectives.Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Oct 18;11(20):2760. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11202760. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37893833 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial intelligence in dentistry and dental biomaterials.Front Dent Med. 2024 Dec 23;5:1525505. doi: 10.3389/fdmed.2024.1525505. eCollection 2024. Front Dent Med. 2024. PMID: 39917699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AI in Orthodontics: Revolutionizing Diagnostics and Treatment Planning-A Comprehensive Review.J Clin Med. 2024 Jan 7;13(2):344. doi: 10.3390/jcm13020344. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38256478 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Shahmoradi L, Safdari R, Mirhosseini MM, Arji G, Jannat B, Abdar M. Predicting risk of acute appendicitis: a comparison of artificial neural network and logistic regression models predicting risk of acute appendicitis: a comparison of artificial neural network and logistic regression models. Acta Med Iran. 2018;56:784–95.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
