Design, synthesis, biological evaluation and molecular docking studies of novel pleuromutilin derivatives containing nitrogen heterocycle and alkylamine groups
- PMID: 35875944
- PMCID: PMC9318235
- DOI: 10.1080/14756366.2022.2104267
Design, synthesis, biological evaluation and molecular docking studies of novel pleuromutilin derivatives containing nitrogen heterocycle and alkylamine groups
Abstract
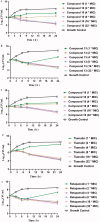
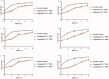
A series of pleuromutilin derivatives containing alkylamine and nitrogen heterocycle groups were designed and synthesised under mild conditions. The in vitro antibacterial activity of these semisynthetic derivatives against four strains of Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA ATCC 43300, S.aureus ATCC 29213, S.aureus AD3, and S.aureus 144) were evaluated by the broth dilution method. Compound 13 was found to have excellent antibacterial activity against MRSA (MIC = 0.0625 μg/mL). Furthermore, compound 13 was further studied by the time-killing kinetics and the post-antibiotic effect approach. In the mouse thigh infection model, compound 13 exhibited superior antibacterial efficacy than that of tiamulin. Meanwhile, compound 13 showed a lower inhibitory effect than that of tiamulin on RAW264.7 and 16HBE cells at the concentration of 10 μg/mL. Molecular docking study revealed that compound 13 can effectively bind to the active site of the 50S ribosome (the binding free energy = -9.66 kcal/mol).
Keywords: MRSA; Pleuromutilin; alkylamine; antibacterial activity; molecular docking; nitrogen heterocycles.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures





Similar articles
-
Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel pleuromutilin derivatives as potent anti-MRSA agents targeting the 50S ribosome.Bioorg Med Chem. 2021 May 15;38:116138. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2021.116138. Epub 2021 Apr 2. Bioorg Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33857737
-
Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel pleuromutilin derivatives possessing 4-aminothiophenol linker as promising antibacterial agents.Bioorg Chem. 2022 Sep;126:105859. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2022.105859. Epub 2022 May 10. Bioorg Chem. 2022. PMID: 35605553
-
Semisynthetic pleuromutilin antimicrobials with therapeutic potential against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by targeting 50S ribosomal subunit.Eur J Med Chem. 2022 Jul 5;237:114341. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114341. Epub 2022 Apr 12. Eur J Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35430480
-
Recent advances in developing modified C14 side chain pleuromutilins as novel antibacterial agents.Eur J Med Chem. 2024 Apr 5;269:116313. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2024.116313. Epub 2024 Mar 15. Eur J Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38503168 Review.
-
Pleuromutilins: Potent Drugs for Resistant Bugs-Mode of Action and Resistance.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2017 Jan 3;7(1):a027110. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a027110. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2017. PMID: 27742734 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Design, synthesis, biological evaluation and molecular docking study of novel pleuromutilin derivatives containing substituted benzoxazole as antibacterial agents.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2023 Dec;38(1):2251712. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2023.2251712. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37664987 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lowy FD. Staphylococcus aureus infections. N Engl J Med 1998;339:520–32. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
