Effectiveness and safety of vedolizumab in a matched cohort of elderly and nonelderly patients with inflammatory bowel disease: the IG-IBD LIVE study
- PMID: 35876062
- PMCID: PMC9324100
- DOI: 10.1111/apt.16923
Effectiveness and safety of vedolizumab in a matched cohort of elderly and nonelderly patients with inflammatory bowel disease: the IG-IBD LIVE study
Abstract
Background: Vedolizumab registration trials were the first to include elderly patients with moderate-to-severe ulcerative colitis (UC) or Crohn's disease (CD), but few real-life data have been reported in this population.
Aims: We investigated the effectiveness and safety of vedolizumab in matched cohorts of elderly and nonelderly UC and CD patients.
Methods: The Long-term Italian Vedolizumab Effectiveness (LIVE) study is a retrospective-prospective study including UC and CD patients who started vedolizumab from April 2016 to June 2017. Elderly patients (≥65 years) were matched clinically 1:2 to nonelderly patients (18-64 years); the 2 groups were followed until drug discontinuation or June 2019.
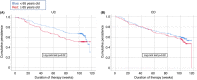
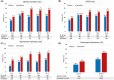
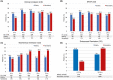
Results: The study included 198 elderly (108 UC, 90 CD) and 396 matched nonelderly patients (205 UC, 191 CD). Nonelderly UC patients had a significantly higher persistence on vedolizumab compared to elderly patients (67.6% vs. 51.4%, p = 0.02). No significant difference in effectiveness was observed between elderly and nonelderly CD patients (59.4% vs. 52.4%, p = 0.32). Age ≥65 years was associated with lower persistence in UC; for CD, previous exposure to anti-TNF-α agents, Charlson comorbidity index >2 and moderate-to-severe clinical activity at baseline were associated with lower persistence. There were recorded 130 adverse events, with comparable rates between the two groups. A Charlson comorbidity index >2 was associated with an increased risk of adverse events.
Conclusion: Vedolizumab can be considered a safe option in elderly IBD patients. Its effectiveness in elderly UC patients may be reduced, while no age-dependent effect on effectiveness was observed in CD.
Keywords: Crohn’s disease; biologics (IBD); immunosuppression; ulcerative colitis.
© 2022 The Authors. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
Comment in
-
Editorial: effectiveness and safety of vedolizumab in a matched cohort of elderly and non-elderly patients with inflammatory bowel disease - the IG-IBD LIVE study.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2022 Aug;56(4):731-732. doi: 10.1111/apt.16957. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2022. PMID: 35879894 No abstract available.
-
Editorial: effectiveness and safety of vedolizumab in a matched cohort of elderly and non-elderly patients with inflammatory bowel disease-the IG-IBD LIVE study. Authors' reply.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2022 Aug;56(4):733-734. doi: 10.1111/apt.17076. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2022. PMID: 35879901 No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organization . Men, Ageing and Health: Achieving Health Across the Life Span. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2001.
-
- Jeuring SFG, van den Heuvel TRA, Zeegers MP, Hameeteman WH, Romberg‐Camps MJL, Oostenbrug LE, et al. Epidemiology and long‐term outcome of inflammatory bowel disease diagnosed at elderly age—an increasing distinct entity? Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2016;22(6):1425–34. 10.1097/MIB.0000000000000738 - DOI - PubMed
