The first crystal structure of a xylobiose-bound xylobiohydrolase with high functional specificity from the bacterial glycoside hydrolase family 30, subfamily 10
- PMID: 35876256
- PMCID: PMC12279061
- DOI: 10.1002/1873-3468.14454
The first crystal structure of a xylobiose-bound xylobiohydrolase with high functional specificity from the bacterial glycoside hydrolase family 30, subfamily 10
Abstract
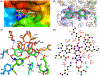
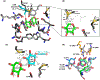
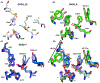
Xylobiose is a prebiotic sugar that has applications in functional foods. This report describes the first X-ray crystallographic structure models of apo and xylobiose-bound forms of a xylobiohydrolase (XBH) from Acetivibrio clariflavus. This xylan-active enzyme, a member of the recently described glycoside hydrolase family 30 (GH30), subfamily 10, phylogenetic clade has been shown to strictly release xylobiose as its primary hydrolysis product. Inspection of the apo structure reveals a glycone region X2 -binding slot. When X2 binds, the non-reducing xylose in the -2 subsite is highly coordinated with numerous hydrogen bond contacts while contacts in the -1 subsite mostly reflect interactions typical for GH30 and enzymes in clan A of the carbohydrate-active enzymes database (CAZy). This structure provides an explanation for the high functional specificity of this new bacterial GH30 XBH subfamily.
Keywords: Acetivibrio clariflavus; GH30_10; cellulosome; glycoside hydrolase; prebiotic; xylobiohydrolase.
Published 2022. This article is a U.S. Government work and is in the public domain in the USA.
Figures


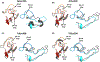
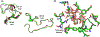
References
-
- Li X, Kouzounis D, Kabel MA, de Vries RP,Dilokpimol A. Glycoside hydrolase family 30 harbors fungal subfamilies with distinct polysaccharide specificities. New Biotechnol. 2022;67:32–41. - PubMed
-
- St John FJ, González JM, Pozharski E. Consolidation of glycosyl hydrolase family 30: a dual domain 4/7 hydrolase family consisting of two structurally distinct groups. FEBS Lett. 2010;584:4435–41. - PubMed
-
- Biely P, Puchart V, Stringer MA, Krogh KB. Trichoderma reesei XYN VI–a novel appendage-dependent eukaryotic glucuronoxylan hydrolase. FEBS J. 2014;281:3894–903. - PubMed
-
- Tenkanen M, Vršanská M, Siika-aho M, Wong DW, Puchart V, Penttilä M, et al. Xylanase XYN IV from Trichoderma reesei showing exo-and endo-xylanase activity. FEBS J. 2013;280:285–301. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

