Limbal-Rigid Contact Lens Wear for the Treatment of Ocular Surface Disorders: A Review
- PMID: 35877181
- PMCID: PMC9298148
- DOI: 10.1097/ICL.0000000000000924
Limbal-Rigid Contact Lens Wear for the Treatment of Ocular Surface Disorders: A Review
Erratum in
-
Erratum to Limbal-Rigid Contact Lens Wear for the Treatment of Ocular Surface Disorders: A Review.Eye Contact Lens. 2022 Oct 1;48(10):448. doi: 10.1097/ICL.0000000000000949. Eye Contact Lens. 2022. PMID: 36155950 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
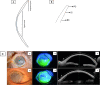
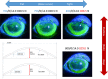
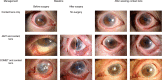
Recently, the prescription of large-diameter rigid gas-permeable contact lenses (CLs), also known as "scleral lenses," "corneoscleral lenses," and "limbal-rigid CLs," is on the rise for the treatment of both moderate and severe ocular surface disorders (OSDs). Compared with scleral lenses, the diameter of limbal-rigid CLs is generally smaller, that is, a diameter ranging from 13.0 to 14.0 mm, and they are designed so that the peripheral edge bears on the limbus. The Suncon Kyoto-CS (Sun Contact Lens Co., Ltd.) is a novel limbal-rigid CL design with multistep curves on the peripheral edge for easy tear exchange during blinking that removes debris and prevents lens clouding or fogging, thus allowing patients to enjoy a longer daily duration of CL wear. In severe OSD cases, limbal-rigid CL wear after surgery is a noninvasive therapeutic approach that can neutralize corneal irregularities, decrease dry eye symptoms, prevent the progression or recurrence of symblepharon, and improve the patient's visual acuity and overall quality of life. Thus, surgeries such as amniotic membrane transplantation and cultivated oral mucosal epithelial transplantation, as well as limbal-rigid CL wear, which is noninvasive, are valuable and effective treatment strategies that can now be applied for the management of patients afflicted with severe OSDs.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the Contact Lens Association of Opthalmologists.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Porcar E, Montalt JC, España-Gregori E, et al. . Fitting scleral lenses less than 15 mm in diameter: A review of the literature. Eye Contact Lens 2020;46:63–69. - PubMed
-
- Nau CB, Harthan J, Shorter E, et al. . Demographic characteristics and prescribing patterns of scleral lens fitters: The scope study. Eye Contact Lens 2018;44:S265–S272. - PubMed
-
- Van der Worp E, Bornman D, Ferreira DL, et al. . Modern scleral contact lenses: A review. Cont Lens Anterior Eye 2014;37:240–250. - PubMed
-
- Michaud L, Lipson M, Kramer E, et al. . The official guide to scleral lens terminology. Cont Lens Anterior Eye 2020;43:529–534. - PubMed
-
- Barnett M, Courey C, Fadel D, et al. . Clear—Scleral lenses. Cont Lens Anterior Eye 2021;44:270–288. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

