Associations between Mobile Internet Use and Self-Rated and Mental Health of the Chinese Population: Evidence from China Family Panel Studies 2020
- PMID: 35877291
- PMCID: PMC9311927
- DOI: 10.3390/bs12070221
Associations between Mobile Internet Use and Self-Rated and Mental Health of the Chinese Population: Evidence from China Family Panel Studies 2020
Abstract
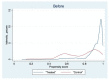
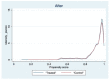
With societal and technological developments, mobile Internet has become the most popular and widespread means to use the Internet in China. Thus, exploring the relationship between mobile Internet use and the self-rated health and mental health of the Chinese population is of great importance. This study empirically examined the impact of mobile Internet use on residents' health using data from the China Family Panel Studies 2020 and conducted a heterogeneity analysis. The results revealed a significant negative association between mobile Internet use and the self-rated health of the population, but a significant positive association was found relative to their mental health. The results of this analysis passed a robustness test. The results of the heterogeneity analysis showed that mobile Internet use had a more significant association with the health of residents with secondary school education and university education compared to those with primary school education or below and graduate education. Furthermore, this study addresses the endogeneity problem using the propensity-score matching model, which is shown to be better at eliminating sample selectivity bias. If endogeneity is not addressed, the negative association with mobile Internet use on residents' self-rated health will be underestimated and its positive association with their mental health will be overestimated. The Chinese government should issue guidelines on the duration of Internet use, strictly regulate exaggerated and harmful content on mobile network platforms, and strengthen people's online skills through training to improve their digital literacy, especially for rural populations.
Keywords: CFPS; China; mental health; mobile Internet use; self-rated health.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of mobile Internet use on the health of middle-aged and older adults: evidences from China health and retirement longitudinal study.BMC Public Health. 2024 Jun 4;24(1):1490. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-18916-w. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38834959 Free PMC article.
-
Residents' Internet use, family economic status, and self-rated health: gender-based differences.BMC Public Health. 2025 Jan 20;25(1):223. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-21371-w. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 39833757 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Internet Use on the Happiness of Chinese Civil Servants: A Mediation Analysis Based on Self-Rated Health.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Oct 12;19(20):13142. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192013142. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36293724 Free PMC article.
-
Association between internet usage and healthcare expenditure among middle-aged and older Chinese adults with chronic diseases: the role of self-rated health.BMC Public Health. 2025 May 28;25(1):1968. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-23195-0. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40437422 Free PMC article.
-
Can Mobile Phone Apps Influence People's Health Behavior Change? An Evidence Review.J Med Internet Res. 2016 Oct 31;18(11):e287. doi: 10.2196/jmir.5692. J Med Internet Res. 2016. PMID: 27806926 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Did internet usage reduce the impact of COVID-19 on the mental health of middle-aged and older adults? A difference-in-differences study based on CFPS data.Front Psychol. 2024 Oct 29;15:1462398. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1462398. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 39534469 Free PMC article.
-
Does the Internet Bring People Closer Together or Further Apart? The Impact of Internet Usage on Interpersonal Communications.Behav Sci (Basel). 2022 Oct 31;12(11):425. doi: 10.3390/bs12110425. Behav Sci (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36354402 Free PMC article.
-
Internet Use and Self-Rated Health: The Mediating Role of Physical Exercise.Healthcare (Basel). 2025 Mar 24;13(7):714. doi: 10.3390/healthcare13070714. Healthcare (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40218012 Free PMC article.
-
How does Internet use impact the mental health of social assistance recipients in China? Examining the chain mediating role of social support and family resilience.Front Psychol. 2025 Jan 6;15:1460064. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1460064. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 39834760 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of mobile Internet use on the health of middle-aged and older adults: evidences from China health and retirement longitudinal study.BMC Public Health. 2024 Jun 4;24(1):1490. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-18916-w. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38834959 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gu H., Wu D. The basic connotation and strategic conception of the high-quality development of the basic medical security system during the “14th Five-Year Plan” period. Manag. World. 2021;37:158–167. doi: 10.19744/j.cnki.11-1235/f.2021.0144. - DOI
-
- Yang L., Song L. A Decomposition Study of the Differences in Healthy Life Expectancy of the Chinese Elderly Population. Popul. Econ. 2022;18:90–105.
-
- Zhong R., Duan L. Xi Jinping’s Important Discourse on Healthy China and Its Significance. Theor. Vis. 2021;3:31–37.
-
- Report of the 19th Congress of the Communist Party of China. [(accessed on 27 October 2017)]; Available online: http://www.gov.cn/zhuanti/2017-10/27/content_5234876.htm.
-
- Highlights of the Communiqué of the Fifth Plenary Session of the Nineteenth Central Committee. [(accessed on 29 October 2020)]. Available online: http://cpc.people.com.cn/n1/2020/1029/c164113-31911575.html.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources