Research on the Mechanism of Influence of Game Competition Mode on Online Learning Performance
- PMID: 35877295
- PMCID: PMC9312023
- DOI: 10.3390/bs12070225
Research on the Mechanism of Influence of Game Competition Mode on Online Learning Performance
Abstract
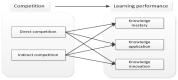
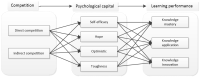
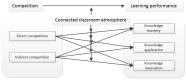
With the rapid development of information technology and the influence of the COVID-19 pandemic, online learning has become an important supplement to the teaching organization form of basic education and higher education. In order to increase user stickiness and improve learning performance, gamification elements are widely introduced into online learning situations. However, scholars have drawn different conclusions on the impact of game-based competition on online learning performance. This study is based on field theory and constructivist learning theory. Taking the online interaction of the curriculum platform as the situation, psychological capital as the intermediary variable and connected classroom atmosphere as the adjustment variable, this paper constructs an interaction model between game competition and online learning performance and discusses in depth the intermediary effect of psychological capital and the adjustment effect of a connected classroom atmosphere. The results show that game-based competition has a significant positive effect on learning performance, and the effect of direct competition is better than that of indirect competition; the self-efficacy dimension of psychological capital plays an intermediary role between direct competition and learning performance, and the resilience dimension plays an intermediary role between competition and learning performance; and a connected classroom atmosphere plays a regulating role in the dimensions of game competition, knowledge mastery and knowledge innovation.
Keywords: competition; curriculum platform; gamification; learning performance; online learning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gamification in Action: Theoretical and Practical Considerations for Medical Educators.Acad Med. 2018 Jul;93(7):1014-1020. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0000000000002183. Acad Med. 2018. PMID: 29465450
-
Game on: The gamification of the pharmacy classroom.Curr Pharm Teach Learn. 2017 Jan-Feb;9(1):155-159. doi: 10.1016/j.cptl.2016.08.046. Epub 2016 Oct 26. Curr Pharm Teach Learn. 2017. PMID: 29180148 Review.
-
Head to head: The role of academic competition in undergraduate anatomical education.Anat Sci Educ. 2015 Sep-Oct;8(5):404-12. doi: 10.1002/ase.1498. Epub 2014 Oct 15. Anat Sci Educ. 2015. PMID: 25319077
-
Eleven game elements for female nonadaptive gamification courses.Heliyon. 2022 Dec 31;9(1):e12699. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e12699. eCollection 2023 Jan. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36632100 Free PMC article.
-
[Game-based approaches to prevention and health promotion: serious games and gamification].Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz. 2020 Jun;63(6):698-707. doi: 10.1007/s00103-020-03156-1. Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz. 2020. PMID: 32451596 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Turning stories into learning journeys: the principles and methods of Immersive Education.Front Psychol. 2024 Dec 6;15:1471459. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1471459. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 39712545 Free PMC article.
-
Experiences of Middle School Programming in an Online Learning Environment.Behav Sci (Basel). 2022 Nov 21;12(11):466. doi: 10.3390/bs12110466. Behav Sci (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36421762 Free PMC article.
-
Parental Phubbing and Adolescent Depressive Symptoms during COVID-19: A Serial Meditating Model.Behav Sci (Basel). 2023 Apr 30;13(5):371. doi: 10.3390/bs13050371. Behav Sci (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37232608 Free PMC article.
-
A Correlation Analysis between Undergraduate Students' Safety Behaviors in the Laboratory and Their Learning Efficiencies.Behav Sci (Basel). 2023 Feb 2;13(2):127. doi: 10.3390/bs13020127. Behav Sci (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36829356 Free PMC article.
References
-
- China Internet Network Information Center . The 47th Statistical Report on Internet Development in China. China Internet Network Information Center; Beijing, China: 2021.
-
- Ortega-Arranz A., Botel-Lorenzo M.L., Asensio-Perez J.I. To reward and be yond: Analyzing the effect of reward-based strategies in a MOOC. Comput. Educ. 2019;142:103639. doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2019.103639. - DOI
-
- Wang W., Guo L., He L. Effects of social-interactive engagement on the dropout ratio in online learning: Insights from MOOC. Behav. Inf. Technol. 2019;38:621–636. doi: 10.1080/0144929X.2018.1549595. - DOI
-
- Sun T., Sheu S. An analysis of factors affecting MOOC learners’ continuous learning: A review of CNKI’s empirical research (2011–2016) Distance Educ. China. 2017;10:55–62, 80.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources