Different Neural Activities for Actions and Language within the Shared Brain Regions: Evidence from Action and Verb Generation
- PMID: 35877314
- PMCID: PMC9312291
- DOI: 10.3390/bs12070243
Different Neural Activities for Actions and Language within the Shared Brain Regions: Evidence from Action and Verb Generation
Abstract
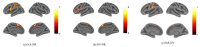
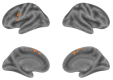
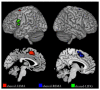
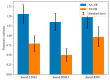
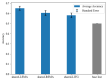
The Inferior Frontal Gyrus, Premotor Cortex and Inferior Parietal Lobe were suggested to be involved in action and language processing. However, the patterns of neural activities in the shared neural regions are still unclear. This study designed an fMRI experiment to analyze the neural activity associations between action and verb generation for object nouns. Using noun reading as a control task, we compared the differences and similarities of brain regions activated by action and verb generation. The results showed that the action generation task activated more in the dorsal Premotor Cortex (PMC), parts of the midline of PMC and the left Inferior Parietal Lobe (IPL) than the verb generation task. Subregions in the bilateral Supplementary Motor Area (SMA) and the left Inferior Frontal Gyrus (IFG) were found to be shared by action and verb generation. Then, mean activation level analysis and multi-voxel pattern analysis (MVPA) were performed in the overlapping activation regions of two generation tasks in the shared regions. The bilateral SMA and the left IFG were found to have overlapping activations with action and verb generation. All the shared regions were found to have different activation patterns, and the mean activation levels of the shared regions in the bilateral of SMA were significantly higher in the action generation. Based on the function of these brain regions, it can be inferred that the shared regions in the bilateral SMA and the left IFG process action and language generation in a task-specific and intention-specific manner, respectively.
Keywords: MVPA; action; fMRI; inferior frontal gyrus; language; supplementary motor area.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Different Neural Information Flows Affected by Activity Patterns for Action and Verb Generation.Front Psychol. 2022 Mar 24;13:802756. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.802756. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 35401310 Free PMC article.
-
Research of cerebral activation in Uygur-speaking and Chinese-speaking participants during verb generation task with functional magnetic resonance imaging.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Jul;96(30):e7460. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000007460. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 28746187 Free PMC article.
-
Neural Activity During Mental Rotation in Deaf Signers: The Influence of Long-Term Sign Language Experience.Ear Hear. 2018 Sep/Oct;39(5):1015-1024. doi: 10.1097/AUD.0000000000000540. Ear Hear. 2018. PMID: 29298164
-
Nouns and verbs in the brain: grammatical class and task specific effects as revealed by fMRI.Cogn Neuropsychol. 2008 Jun;25(4):528-58. doi: 10.1080/02643290701674943. Cogn Neuropsychol. 2008. PMID: 19086201
-
Noun and verb retrieval by normal subjects. Studies with PET.Brain. 1996 Feb;119 ( Pt 1):159-79. doi: 10.1093/brain/119.1.159. Brain. 1996. PMID: 8624678 Review.
Cited by
-
Why multiple intelligences theory is a neuromyth.Front Psychol. 2023 Aug 28;14:1217288. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1217288. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 37701872 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Glenberg A.M., Kaschak M.P. Grounding language in action. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2002;9:558–565. - PubMed
-
- Hauk O., Johnsrude I., Pulvermüller F. Somatotopic representation of action words in human motor and premotor cortex. Neuron. 2004;41:301–307. - PubMed
-
- Aziz-Zadeh L., Wilson S.M., Rizzolatti G., Iacoboni M. Congruent embodied representations for visually presented actions and linguistic phrases describing actions. Curr. Biol. 2006;16:1818–1823. - PubMed
-
- Grabowski T.J., Damasio H., Damasio A.R. Premotor and prefrontal correlates of category-related lexical retrieval. Neuroimage. 1998;7:232–243. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

