Anti-EpCAM Functionalized I-131 Radiolabeled Biomimetic Nanocarrier Sodium/Iodide-Symporter-Mediated Breast-Cancer Treatment
- PMID: 35877345
- PMCID: PMC9311516
- DOI: 10.3390/bioengineering9070294
Anti-EpCAM Functionalized I-131 Radiolabeled Biomimetic Nanocarrier Sodium/Iodide-Symporter-Mediated Breast-Cancer Treatment
Abstract
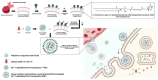
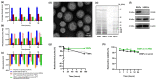
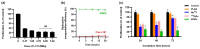
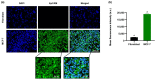
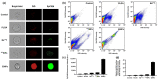
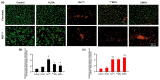
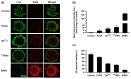
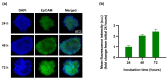
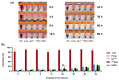
Currently, breast-cancer treatment has a number of adverse side effects and is associated with poor rates of progression-free survival. Therefore, a radiolabeled anti-EpCAM targeted biomimetic coated nanocarrier (EINP) was developed in this study to overcome some of the treatment challenges. The double emulsion method synthesized the poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) nanoparticle with Na131I entrapped in the core. The PLGA nanoparticle was coated in human red blood cell membranes and labeled with epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) antibody to enable it to target EpCAM overexpression by breast-cancer cells. Characterization determined the EINP size as 295 nm, zeta potential as −35.9 mV, and polydispersity as 0.297. EINP radiochemical purity was >95%. Results determined the EINP efficacy against EpCAM positive MCF-7 breast cancer at 24, 48, and 72 h were 69.11%, 77.84%, and 74.6%, respectively, demonstrating that the EINPs achieved greater cytotoxic efficacy supported by NIS-mediated Na131I uptake than the non-targeted 131INPs and Na131I. In comparison, fibroblast (EpCAM negative) treated with EINPs had significantly lower cytotoxicity than Na131I and 131INPs (p < 0.05). Flow cytometry fluorescence imaging visually signified delivery by EINPs specifically to breast-cancer cells as a result of anti-EpCAM targeting. Additionally, the EINP had a favorable safety profile, as determined by hemolysis.
Keywords: EpCAM; I-131; PLGA; breast cancer; drug delivery; ionizing radiation; nanoparticle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Runowicz C.D., Leach C.R., Henry N.L., Henry K.S., Mackey H.T., Cowens-Alvarado R.L., Cannady R.S., Pratt-Chapman M.L., Edge S.B., Jacobs L.A. American Cancer Society/American Society of Clinical Oncology Breast Cancer Survivorship Care Guideline. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2016;66:43–73. doi: 10.3322/caac.21319. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Brito A.F., Abrantes A.M., Teixo R., Pires A.S., Ribeiro A.C., Ferreira R.F., Mascarenhas A., Puga T., Laranjo M., Caramelo F. Iodine-131 Metabolic Radiotherapy Leads to Cell Death and Genomic Alterations through NIS Overexpression on Cholangiocarcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2020;56:709–727. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2020.4957. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Spitzweg C., Zhang S., Bergert E.R., Castro M.R., McIver B., Heufelder A.E., Tindall D.J., Young C.Y., Morris J.C. Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Promoter-Driven Androgen-Inducible Expression of Sodium Iodide Symporter in Prostate Cancer Cell Lines. Cancer Res. 1999;59:2136–2141. - PubMed
-
- Huang M., Batra R.K., Kogai T., Lin Y.Q., Hershman J.M., Lichtenstein A., Sharma S., Zhu L.X., Brent G.A., Dubinett S.M. Ectopic Expression of the Thyroperoxidase Gene Augments Radioiodide Uptake and Retention Mediated by the Sodium Iodide Symporter in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Gene Ther. 2001;8:612–618. doi: 10.1038/sj.cgt.7700354. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

