TNF-α Suppresses Apelin Receptor Expression in Mouse Quadriceps Femoris-Derived Cells
- PMID: 35877441
- PMCID: PMC9315797
- DOI: 10.3390/cimb44070217
TNF-α Suppresses Apelin Receptor Expression in Mouse Quadriceps Femoris-Derived Cells
Abstract
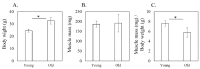
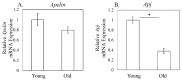
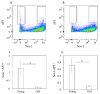
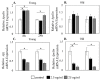
Expression of the apelin receptor, APJ, in skeletal muscle (SM) is known to decrease with age, but the underlying mechanism remains unclear. Increased tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α levels are observed in SM with age and are associated with muscle atrophy. To investigate the possible interconnection between TNF-α elevation and APJ reduction with aging, we investigated the effect of TNF-α on APJ expression in cells derived from the quadriceps femoris of C57BL/6J mice. Expression of Tnfa and Apj in the quadriceps femoris was compared between 4- (young) and 24-month-old (old) C57BL/6J mice (n = 10 each) using qPCR. Additionally, APJ-positive cells and TNF-α protein were analyzed by flow cytometry and Western blotting, respectively. Further, quadricep-derived cells were exposed to 0 (control) or 25 ng/mL TNF-α, and the effect on Apj expression was examined by qRT-PCR. Apj expression and the ratio of APJ-positive cells among quadricep cells were significantly lower in old compared to young mice. In contrast, levels of Tnfa mRNA and TNF-α protein were significantly elevated in old compared to young mice. Exposing young and old derived quadricep cells to TNF-α for 8 and 24 h caused Apj levels to significantly decrease. TNF-α suppresses APJ expression in muscle cells in vitro. The increase in TNF-α observed in SM with age may induce a decrease in APJ expression.
Keywords: TNF-α; aging; apelin receptor (APJ); skeletal muscle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Cruz-Jentoft A.J., Baeyens J.P., Bauer J.M., Boirie Y., Cederholm T., Landi F., Martin F.C., Michel J.P., Rolland Y., Schneider S.M., et al. Sarcopenia: European consensus on definition and diagnosis: Report of the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People. Age Ageing. 2010;39:412–423. doi: 10.1093/ageing/afq034. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Murphy R.A., Ip E.H., Zhang Q., Boudreau R.M., Cawthon P.M., Newman A.B., Tylavsky F.A., Visser M., Goodpaster B.H., Harris T.B., et al. Transition to sarcopenia and determinants of transitions in older adults: A population-based study. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2014;69:751–758. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glt131. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

