Synthesis and Characterization of Chitosan-Decorated Nanoemulsion Gel of 5-Fluorouracil for Topical Delivery
- PMID: 35877497
- PMCID: PMC9318027
- DOI: 10.3390/gels8070412
Synthesis and Characterization of Chitosan-Decorated Nanoemulsion Gel of 5-Fluorouracil for Topical Delivery
Abstract
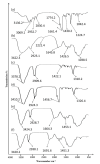
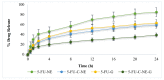
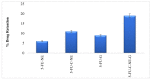
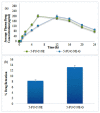
(1) Background: The present study aimed to prepare chitosan-coated nanoemulsion gel containing 5-fluorouracil for enhanced topical delivery. (2) Methods: To formulate the nanoemulsion gel, oleic acid was used as the oil phase and Carbopol 940 as a gelling agent. Chitosan was used as a coating agent to control the release of 5-FU. Drug−excipient compatibility was evaluated using ATR-FTIR. The prepared nanoemulsion formulations were characterized based on particle size distribution, zeta potential, % encapsulation efficiency and drug content. In vitro drug release, skin drug retention and ex vivo permeation profiles were performed across rat skin using a Franz diffusion cell. Skin irritation experiments were also conducted on rats to examine the irritation potential of the formulations. (3) Results: It was found that the drug and excipients were compatible and chitosan successfully coated 5-FU, as demonstrated by ATR-FTIR results. The introduction of chitosan increased the size and zeta potential of the nanoemulsion. The 5-FU release in vitro was significantly lowered in the case of chitosan-decorated nanoemulsion (5-FU-C-NE), whereas the permeation and skin drug retention were higher in the case of 5-FU-C-NE. The formulations were proven non-irritant to the skin of the rats. The optimized formulation of the nanoemulsion was introduced into 1% Carbopol 940 gel. Incorporating the nanoemulsion into the gel further reduced the drug release in vitro and ex vivo permeation, whereas the retention of the drug in the skin was significantly increased (ANOVA; p < 0.05). The increase in skin retention was due to the presence of chitosan and Carbopol 940. The in vitro and ex vivo results were also confirmed with in vivo studies. Incorporating nanoemulsion into gel has resulted in higher Tmax, longer half-life and greater skin drug retention. (4) Conclusion: The results suggest that chitosan-decorated nanoemulsion gel is safe and can potentially be used to promote 5-FU skin retention, which is ideal for skin diseases such as melanoma.
Keywords: 5-fluorouracil; chitosan; gel; nanoemulsion; topical delivery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Formulation Development and In Vitro/In Vivo Characterization of Methotrexate-Loaded Nanoemulsion Gel Formulations for Enhanced Topical Delivery.Gels. 2022 Dec 22;9(1):3. doi: 10.3390/gels9010003. Gels. 2022. PMID: 36661771 Free PMC article.
-
Lornoxicam-Loaded Chitosan-Decorated Nanoemulsion: Preparation and In Vitro Evaluation for Enhanced Transdermal Delivery.Polymers (Basel). 2022 May 9;14(9):1922. doi: 10.3390/polym14091922. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35567091 Free PMC article.
-
A comparative ex vivo permeation evaluation of a novel 5-Fluorocuracil nanoemulsion-gel by topically applied in the different excised rat, goat, and cow skin.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2020 Apr;27(4):1024-1040. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2020.02.014. Epub 2020 Mar 3. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32256163 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Update on Nanoemulsion Impregnated Hydrogel: a Gleam into the Revolutionary Strategy for Diffusion-Controlled Delivery of Therapeutics.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2023 Jul 12;24(6):151. doi: 10.1208/s12249-023-02611-x. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2023. PMID: 37438613 Review.
-
Enhancing vaginal drug delivery: the nanoemulsion gel strategy.Z Naturforsch C J Biosci. 2025 Feb 27. doi: 10.1515/znc-2024-0239. Online ahead of print. Z Naturforsch C J Biosci. 2025. PMID: 40010933 Review.
Cited by
-
Multi-omics profiling of retinal pigment epithelium reveals enhancer-driven activation of RANK-NFATc1 signaling in traumatic proliferative vitreoretinopathy.Nat Commun. 2024 Aug 25;15(1):7324. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-51624-y. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39183203 Free PMC article.
-
Thermosensitive Hydrogels Loaded with Resveratrol Nanoemulsion: Formulation Optimization by Central Composite Design and Evaluation in MCF-7 Human Breast Cancer Cell Lines.Gels. 2022 Jul 19;8(7):450. doi: 10.3390/gels8070450. Gels. 2022. PMID: 35877535 Free PMC article.
-
Development and evaluation of Resveratrol-loaded liposomes in hydrogel-based wound dressing for diabetic foot ulcer.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023 Aug;396(8):1811-1825. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02441-5. Epub 2023 Mar 2. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36862150
-
Synthesis of fungal polysaccharide-based nanoemulsions for cancer treatment.RSC Adv. 2025 Apr 25;15(17):13300-13312. doi: 10.1039/d5ra01349f. eCollection 2025 Apr 22. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40290748 Free PMC article.
-
A poly-δ-decalactone (PDL) based nanoemulgel for topical delivery of ketoconazole and eugenol against Candida albicans.Nanoscale Adv. 2024 Aug 2;6(21):5322-36. doi: 10.1039/d4na00176a. Online ahead of print. Nanoscale Adv. 2024. PMID: 39247866 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bozorg B.D., Bhattaccharjee S.A., Somayaji M.R., Banga A.K. Topical and transdermal delivery with diseased human skin: Passive and iontophoretic delivery of hydrocortisone into psoriatic and eczematous skin. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2022;12:197–212. doi: 10.1007/s13346-021-00897-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pourmanouchehri Z., Ebrahimi S., Limoee M., Jalilian F., Janfaza S., Vosoughi A., Behbood L. Controlled release of 5-fluorouracil to melanoma cells using a hydrogel/micelle composites based on deoxycholic acid and carboxymethyl chitosan. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022;206:159–166. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.02.096. - DOI - PubMed
-
- de Oliveira B.E., Amorim O.H.J., Lima L.L., Rezende R.A., Mestnik N.C., Bagatin E., Leonardi G.R. 5-Fluorouracil, innovative drug delivery systems to enhance bioavailability for topical use. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021;61:102155. doi: 10.1016/j.jddst.2020.102155. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

