Assessing model adequacy for Bayesian Skyline plots using posterior predictive simulation
- PMID: 35877611
- PMCID: PMC9312427
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0269438
Assessing model adequacy for Bayesian Skyline plots using posterior predictive simulation
Abstract
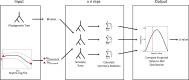
Bayesian skyline plots (BSPs) are a useful tool for making inferences about demographic history. For example, researchers typically apply BSPs to test hypotheses regarding how climate changes have influenced intraspecific genetic diversity over time. Like any method, BSP has assumptions that may be violated in some empirical systems (e.g., the absence of population genetic structure), and the naïve analysis of data collected from these systems may lead to spurious results. To address these issues, we introduce P2C2M.Skyline, an R package designed to assess model adequacy for BSPs using posterior predictive simulation. P2C2M.Skyline uses a phylogenetic tree and the log file output from Bayesian Skyline analyses to simulate posterior predictive datasets and then compares this null distribution to statistics calculated from the empirical data to check for model violations. P2C2M.Skyline was able to correctly identify model violations when simulated datasets were generated assuming genetic structure, which is a clear violation of BSP model assumptions. Conversely, P2C2M.Skyline showed low rates of false positives when models were simulated under the BSP model. We also evaluate the P2C2M.Skyline performance in empirical systems, where we detected model violations when DNA sequences from multiple populations were lumped together. P2C2M.Skyline represents a user-friendly and computationally efficient resource for researchers aiming to make inferences from BSP.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Gelman A. A Bayesian formulation of exploratory data analysis and goodness-of-fit testing. Int Stat Rev. 2003;71(2):369–82.
-
- Carstens BC, Smith ML, Duckett DJ, Fonseca EM, Thomé MTC. Assessing model adequacy leads to more robust phylogeographic inference. Trends Ecol Evol [Internet]. 2022. Jan; Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0169534721003426. doi: 10.1016/j.tree.2021.12.007 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

