Amphiphilic Gold Nanoparticles: A Biomimetic Tool to Gain Mechanistic Insights into Peptide-Lipid Interactions
- PMID: 35877876
- PMCID: PMC9324301
- DOI: 10.3390/membranes12070673
Amphiphilic Gold Nanoparticles: A Biomimetic Tool to Gain Mechanistic Insights into Peptide-Lipid Interactions
Abstract
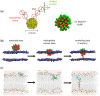
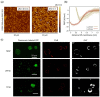
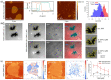
Functional peptides are now widely used in a myriad of biomedical and clinical contexts, from cancer therapy and tumor targeting to the treatment of bacterial and viral infections. Underlying this diverse range of applications are the non-specific interactions that can occur between peptides and cell membranes, which, in many contexts, result in spontaneous internalization of the peptide within cells by avoiding energy-driven endocytosis. For this to occur, the amphipathicity and surface structural flexibility of the peptides play a crucial role and can be regulated by the presence of specific molecular residues that give rise to precise molecular events. Nevertheless, most of the mechanistic details regulating the encounter between peptides and the membranes of bacterial or animal cells are still poorly understood, thus greatly limiting the biomimetic potential of these therapeutic molecules. In this arena, finely engineered nanomaterials-such as small amphiphilic gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) protected by a mixed thiol monolayer-can provide a powerful tool for mimicking and investigating the physicochemical processes underlying peptide-lipid interactions. Within this perspective, we present here a critical review of membrane effects induced by both amphiphilic AuNPs and well-known amphiphilic peptide families, such as cell-penetrating peptides and antimicrobial peptides. Our discussion is focused particularly on the effects provoked on widely studied model cell membranes, such as supported lipid bilayers and lipid vesicles. Remarkable similarities in the peptide or nanoparticle membrane behavior are critically analyzed. Overall, our work provides an overview of the use of amphiphilic AuNPs as a highly promising tailor-made model to decipher the molecular events behind non-specific peptide-lipid interactions and highlights the main affinities observed both theoretically and experimentally. The knowledge resulting from this biomimetic approach could pave the way for the design of synthetic peptides with tailored functionalities for next-generation biomedical applications, such as highly efficient intracellular delivery systems.
Keywords: antimicrobial peptides; cell membranes; cell-penetrating peptides; lipid bilayers; molecular dynamics; non-specific interactions; spontaneous membrane translocation; thiol-protected gold nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Gold nanoparticles interacting with synthetic lipid rafts: an AFM investigation.J Microsc. 2020 Dec;280(3):194-203. doi: 10.1111/jmi.12910. Epub 2020 Jun 2. J Microsc. 2020. PMID: 32432336
-
Aromaticity/Bulkiness of Surface Ligands to Promote the Interaction of Anionic Amphiphilic Gold Nanoparticles with Lipid Bilayers.Langmuir. 2016 Feb 16;32(6):1601-10. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.6b00035. Epub 2016 Feb 3. Langmuir. 2016. PMID: 26794292
-
Behavior of Citrate-Capped Ultrasmall Gold Nanoparticles on a Supported Lipid Bilayer Interface at Atomic Resolution.ACS Nano. 2022 Oct 25;16(10):17179-17196. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.2c07751. Epub 2022 Sep 19. ACS Nano. 2022. PMID: 36121776
-
Plasmonic Nanoparticle-Interfaced Lipid Bilayer Membranes.Acc Chem Res. 2019 Oct 15;52(10):2793-2805. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.9b00327. Epub 2019 Sep 25. Acc Chem Res. 2019. PMID: 31553568 Review.
-
How Membrane-Active Peptides Get into Lipid Membranes.Acc Chem Res. 2016 Jun 21;49(6):1130-8. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.6b00074. Epub 2016 May 17. Acc Chem Res. 2016. PMID: 27187572 Review.
References
-
- Wang X.-Y., Wang Y.-H., Song Z., Hu X.-Y., Wei J.-P., Zhang J., Wang H.-S. Recent Progress in Functional Peptides Designed for Tumor-Targeted Imaging and Therapy. J. Mater. Chem. C. 2021;9:3749–3772. doi: 10.1039/D0TC05405D. - DOI
-
- Rong L., Qin S.-Y., Zhang C., Cheng Y.-J., Feng J., Wang S.-B., Zhang X.-Z. Biomedical Applications of Functional Peptides in Nano-Systems. Mater. Today Chem. 2018;9:91–102. doi: 10.1016/j.mtchem.2018.06.001. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

