Progress for Co-Incorporation of Polydopamine and Nanoparticles for Improving Membranes Performance
- PMID: 35877880
- PMCID: PMC9317275
- DOI: 10.3390/membranes12070675
Progress for Co-Incorporation of Polydopamine and Nanoparticles for Improving Membranes Performance
Abstract
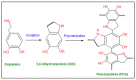
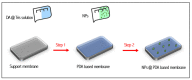
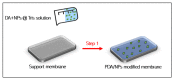
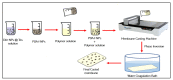
Incorporating polydopamine has become a viable method for membrane modification due to its universality and versatility. Fillers in their different categories have been confirmed as effective elements to improve the properties of membranes such as hydrophilicity, permeability, mechanical strength, and fouling resistance. Thus, this paper mainly highlights the recent studies that have been carried out using polydopamine and nanomaterial fillers simultaneously in modifying the performance of different membranes such as ultrafiltration, microfiltration, nanofiltration, reverse osmosis, and forward osmosis membranes according to the various modification methods. Graphene oxide nanoparticles have recently attracted a lot of attention among different nanoparticles used with polydopamine, due to their impressive characteristics impacts on enhancing membrane hydrophilicity, mechanical strength, and fouling resistance. Thus, the incorporation techniques of graphene oxide nanoparticles and polydopamine for enhancing membranes have been highlighted in this work. Moreover, different studies carried out on using polydopamine as a nanofiller for optimizing membrane performance have been discussed. Finally, perspectives, and possible paths of further research on mussel-inspired polydopamine and nanoparticles co-incorporation are stated according to the progress made in this field. It is anticipated that this review would provide benefits for the scientific community in designing a new generation of polymeric membranes for the treatment of different feed water and wastewater based on adhesive mussel inspired polydopamine polymer and nanomaterials combinations.
Keywords: dopamine; membranes; mussel-inspired chemistry; nanoparticles; polydopamine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

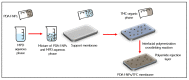
Similar articles
-
Copper-Modified Polymeric Membranes for Water Treatment: A Comprehensive Review.Membranes (Basel). 2021 Jan 28;11(2):93. doi: 10.3390/membranes11020093. Membranes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33525631 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanocomposite Membranes via the Codeposition of Polydopamine/Polyethylenimine with Silica Nanoparticles for Enhanced Mechanical Strength and High Water Permeability.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017 Jan 25;9(3):2966-2972. doi: 10.1021/acsami.6b13761. Epub 2017 Jan 9. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017. PMID: 28001040
-
Mussel-Inspired Architecture of High-Flux Loose Nanofiltration Membrane Functionalized with Antibacterial Reduced Graphene Oxide-Copper Nanocomposites.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017 Aug 30;9(34):28990-29001. doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b05930. Epub 2017 Aug 16. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017. PMID: 28767226
-
Insights into the impact of polydopamine modification on permeability and anti-fouling performance of forward osmosis membrane.Chemosphere. 2022 Mar;291(Pt 1):132744. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132744. Epub 2021 Oct 29. Chemosphere. 2022. PMID: 34743795
-
Progress of Nanocomposite Membranes for Water Treatment.Membranes (Basel). 2018 Apr 3;8(2):18. doi: 10.3390/membranes8020018. Membranes (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29614045 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Comprehensive Review of Performance of Polyacrylonitrile-Based Membranes for Forward Osmosis Water Separation and Purification Process.Membranes (Basel). 2023 Nov 3;13(11):872. doi: 10.3390/membranes13110872. Membranes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37999358 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advanced Polymeric Nanocomposite Membranes for Water and Wastewater Treatment: A Comprehensive Review.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Jan 20;15(3):540. doi: 10.3390/polym15030540. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36771842 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hafiz M.A.N. Ph.D. Thesis. Volume 52 Qatar University; Doha, Qatar: 2019. Engineering a Fertilizing Draw Solution for Irrigation Using Forward Osmosis/Reverse Osmosis Hybrid System.
-
- Wang J., Liu X. Forward Osmosis Technology for Water Treatment: Recent Advances and Future Perspectives. J. Clean. Prod. 2020;280:124354. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124354. - DOI
-
- Islam M.S., Touati K., Rahaman M.S. High Flux and Antifouling Thin-Film Nanocomposite Forward Osmosis Membrane with Ingrained Silica Nanoparticles. ACS ES&T Eng. 2021;1:467–477. doi: 10.1021/acsestengg.0c00177. - DOI
-
- Rezaei-DashtArzhandi M., Sarrafzadeh M.H., Goh P.S., Lau W.J., Ismail A.F., Mohamed M.A. Development of Novel Thin Film Nanocomposite Forward Osmosis Membranes Containing Halloysite/Graphitic Carbon Nitride Nanoparticles towards Enhanced Desalination Performance. Desalination. 2018;447:18–28. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2018.08.003. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

