A Novel Anaerobic Gravity-Driven Dynamic Membrane Bioreactor (AnGDMBR): Performance and Fouling Characterization
- PMID: 35877886
- PMCID: PMC9351681
- DOI: 10.3390/membranes12070683
A Novel Anaerobic Gravity-Driven Dynamic Membrane Bioreactor (AnGDMBR): Performance and Fouling Characterization
Abstract
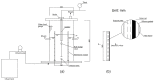
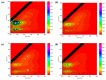
Despite numerous studies undertaken to define the development and significance of the dynamic membrane (DM) formed on some coarse materials, the optimization of reactor configuration and the control of the membrane fouling of anaerobic dynamic membrane bioreactor (AnDMBR) need to be further investigated. The aim of this study was to design a novel anaerobic gravity-driven dynamic membrane bioreactor (AnGDMBR) for the effective and low-cost treatment of municipal wastewater. An 800 mesh nylon net was determined as the optimal support material based on its less irreversible fouling and higher effluent quality by the dead-end filtration experiments. During the continuous operation period of 44 days, the reactor performance, DM filtration behavior and microbial characteristics were studied and compared with the results of recent studies. AnGDMBR had a higher removal rate of chemical oxygen demand (COD) of 85.45 ± 7.06%. Photometric analysis integrating with three-dimensional excitation-emission matrix fluorescence spectra showed that the DM effectively intercepted organics (46.34 ± 16.50%, 75.24 ± 17.35%, and 66.39 ± 17.66% for COD, polysaccharides, and proteins). The addition of suspended carriers effectively removed the DM layer by mechanical scouring, and the growth rate of transmembrane pressure (TMP) and the decreasing rate of flux were reduced from 18.7 to 4.7 Pa/h and 0.07 to 0.01 L/(m2·h2), respectively. However, a dense and thin morphological structure of the DM layer was still observed in the end of reactor operation and plenty of filamentous microorganisms (i.e., SJA-15 and Anaerolineaceae) and the acidogens (i.e., Aeromonadaceae) predominated in the DM layer, which was also embedded in the membrane pore and led to severe irreversible fouling. In summary, the novel AnGDMBR has a superior performance (higher organic removal and lower fouling rates), which provides useful information on the configuration and operation of AnDMBRs for municipal wastewater treatment.
Keywords: cake layer; irreversible fouling; membrane bioreactor; non-woven fabric; nylon net.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Process optimization and filtration performance of an anaerobic dynamic membrane bioreactor treating textile wastewaters.J Environ Manage. 2020 Nov 1;273:111114. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111114. Epub 2020 Jul 29. J Environ Manage. 2020. PMID: 32738743
-
Anaerobic membrane bioreactor for treatment of synthetic municipal wastewater at ambient temperature.Water Sci Technol. 2007;55(7):79-86. doi: 10.2166/wst.2007.130. Water Sci Technol. 2007. PMID: 17506423
-
Treatment of synthetic wastewater and cheese whey by the anaerobic dynamic membrane bioreactor.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019 Nov;26(32):32942-32956. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-06397-z. Epub 2019 Sep 11. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31512125
-
Periodic fouling control strategies in gravity-driven membrane bioreactors (GD-MBRs): Impact on treatment performance and membrane fouling properties.Sci Total Environ. 2022 Sep 10;838(Pt 3):156340. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.156340. Epub 2022 May 31. Sci Total Environ. 2022. PMID: 35654208
-
Upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor--a review.Indian J Environ Health. 2001 Apr;43(2):1-82. Indian J Environ Health. 2001. PMID: 12397675 Review.
References
-
- Skouteris G., Hermosilla D., López P., Negro C., Blanco Á. Anaerobic membrane bioreactors for wastewater treatment: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2012;198–199:138–148. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2012.05.070. - DOI
-
- Smith A.L., Stadler L.B., Cao L., Love N.G., Raskin L., Skerlos S.J. Navigating Wastewater Energy Recovery Strategies: A Life Cycle Comparison of Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactor and Conventional Treatment Systems with Anaerobic Digestion. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014;48:5972–5981. doi: 10.1021/es5006169. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lin H., Peng W., Zhang M., Chen J., Hong H., Zhang Y. A review on anaerobic membrane bioreactors: Applications, membrane fouling and future perspectives. Desalination. 2013;314:169–188. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2013.01.019. - DOI
-
- Jeison D., van Lier J.B. Cake formation and consolidation: Main factors governing the applicable flux in anaerobic submerged membrane bioreactors (AnSMBR) treating acidified wastewaters. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2007;56:71–78. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2007.01.022. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

