Host-Bacterial Interactions: Outcomes of Antimicrobial Peptide Applications
- PMID: 35877918
- PMCID: PMC9317001
- DOI: 10.3390/membranes12070715
Host-Bacterial Interactions: Outcomes of Antimicrobial Peptide Applications
Abstract
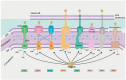
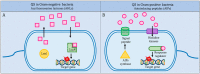
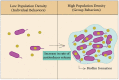
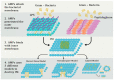
The bacterial membrane is part of a secretion system which plays an integral role to secrete proteins responsible for cell viability and pathogenicity; pathogenic bacteria, for example, secrete virulence factors and other membrane-associated proteins to invade the host cells through various types of secretion systems (Type I to Type IX). The bacterial membrane can also mediate microbial communities' communication through quorum sensing (QS), by secreting auto-stimulants to coordinate gene expression. QS plays an important role in regulating various physiological processes, including bacterial biofilm formation while providing increased virulence, subsequently leading to antimicrobial resistance. Multi-drug resistant (MDR) bacteria have emerged as a threat to global health, and various strategies targeting QS and biofilm formation have been explored by researchers worldwide. Since the bacterial secretion systems play such a crucial role in host-bacterial interactions, this review intends to outline current understanding of bacterial membrane systems, which may provide new insights for designing approaches aimed at antimicrobials discovery. Various mechanisms pertaining interaction of the bacterial membrane with host cells and antimicrobial agents will be highlighted, as well as the evolution of bacterial membranes in evasion of antimicrobial agents. Finally, the use of antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) as a cellular device for bacterial secretion systems will be discussed as emerging potential candidates for the treatment of multidrug resistance infections.
Keywords: antimicrobial peptides; antimicrobial resistance; bacterial membrane; quorum sensing; secreting system.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Developments in strategies for Quorum Sensing virulence factor inhibition to combat bacterial drug resistance.Microb Pathog. 2018 Aug;121:293-302. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2018.05.046. Epub 2018 May 29. Microb Pathog. 2018. PMID: 29857121 Review.
-
Antimicrobial and anti-Quorum Sensing activities of selected medicinal plants of Ethiopia: Implication for development of potent antimicrobial agents.BMC Microbiol. 2016 Jul 11;16(1):139. doi: 10.1186/s12866-016-0765-9. BMC Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27400878 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of quorum sensing to virulence and antibiotic resistance in zoonotic bacteria.Biotechnol Adv. 2022 Oct;59:107965. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2022.107965. Epub 2022 Apr 26. Biotechnol Adv. 2022. PMID: 35487393 Review.
-
Broad-spectrum quorum sensing and biofilm inhibition by green tea against gram-negative pathogenic bacteria: Deciphering the role of phytocompounds through molecular modelling.Microb Pathog. 2019 Jan;126:379-392. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2018.11.030. Epub 2018 Nov 23. Microb Pathog. 2019. PMID: 30476580
-
Quorum sensing pathways in Gram-positive and -negative bacteria: potential of their interruption in abating drug resistance.J Chemother. 2019 Jul;31(4):161-187. doi: 10.1080/1120009X.2019.1599175. Epub 2019 Apr 22. J Chemother. 2019. PMID: 31007147 Review.
Cited by
-
In vivo Pharmacokinetic and ADMET Profiles of Synthetic Antimicrobial Peptides (AMPs).Mini Rev Med Chem. 2025;25(8):579-590. doi: 10.2174/0113895575362479241231054240. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 39950486 Review.
-
In silico directed evolution of Anabas testudineus AtMP1 antimicrobial peptide to improve in vitro anticancer activity.PeerJ. 2024 Sep 26;12:e17894. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17894. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 39346049 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Aspects of the Functioning of Pathogenic Bacteria Biofilm Based on Quorum Sensing (QS) Signal-Response System and Innovative Non-Antibiotic Strategies for Their Elimination.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 24;25(5):2655. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052655. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38473900 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antimicrobial Peptides and Small Molecules Targeting the Cell Membrane of Staphylococcus aureus.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2023 Jun 28;87(2):e0003722. doi: 10.1128/mmbr.00037-22. Epub 2023 Apr 27. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2023. PMID: 37129495 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

