Staphylococcus aureus Alpha-Toxin in Deep Tracheal Aspirates-Preliminary Evidence for Its Presence in the Lungs of Sepsis Patients
- PMID: 35878188
- PMCID: PMC9320683
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins14070450
Staphylococcus aureus Alpha-Toxin in Deep Tracheal Aspirates-Preliminary Evidence for Its Presence in the Lungs of Sepsis Patients
Abstract
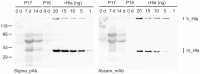
The pore forming alpha-toxin (hemolysin A, Hla) of Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) is a major virulence factor with relevance for the pathogenicity of this bacterium, which is involved in many cases of pneumonia and sepsis in humans. Until now, the presence of Hla in the body fluids of potentially infected humans could only be shown indirectly, e.g., by the presence of antibodies against Hla in serum samples or by hemolysis testing on blood agar plates of bacterial culture supernatants of the clinical isolates. In addition, nothing was known about the concentrations of Hla actually reached in the body fluids of the infected hosts. Western blot analyses on 36 samples of deep tracheal aspirates (DTA) isolated from 22 hospitalized sepsis patients using primary antibodies against different epitopes of the Hla molecule resulted in the identification of six samples from five patients containing monomeric Hla (approx. 33 kDa). Two of these samples showed also signals at the molecular mass of heptameric Hla (232 kDa). Semiquantitative analyses of the samples revealed that the concentrations of monomeric Hla ranged from 16 to 3200 ng/mL. This is, to our knowledge, the first study directly showing the presence of S. aureus Hla in samples of airway surface liquid in human patients.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus; alpha-toxin; deep tracheal aspirate; sepsis patients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Characterization of alpha-toxin hla gene variants, alpha-toxin expression levels, and levels of antibody to alpha-toxin in hemodialysis and postsurgical patients with Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia.J Clin Microbiol. 2015 Jan;53(1):227-36. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02023-14. Epub 2014 Nov 12. J Clin Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25392350 Free PMC article.
-
Candida albicans Augments Staphylococcus aureus Virulence by Engaging the Staphylococcal agr Quorum Sensing System.mBio. 2019 Jun 4;10(3):e00910-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00910-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 31164467 Free PMC article.
-
Novel structurally designed vaccine for S. aureus α-hemolysin: protection against bacteremia and pneumonia.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e38567. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038567. Epub 2012 Jun 6. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22701668 Free PMC article.
-
α-Hemolysin activity of methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus predicts ventilator-associated pneumonia.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014 Nov 15;190(10):1139-48. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201406-1012OC. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014. PMID: 25303310
-
Staphylococcus aureus Alpha-Toxin Is Conserved among Diverse Hospital Respiratory Isolates Collected from a Global Surveillance Study and Is Neutralized by Monoclonal Antibody MEDI4893.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 Aug 22;60(9):5312-21. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00357-16. Print 2016 Sep. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016. PMID: 27324766 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
YjbH contributes to Staphylococcus aureus skin pathology and immune response through Agr-mediated α-toxin regulation.Virulence. 2024 Dec;15(1):2399798. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2024.2399798. Epub 2024 Sep 9. Virulence. 2024. PMID: 39229975 Free PMC article.
References
-
- da Silva M.C., Zahm J.M., Gras D., Bajolet O., Abely M., Hinnrasky J., Milliot M., De Assis M.C., Hologne C., Bonnet N., et al. Dynamic interaction between airway epithelial cells and Staphylococcus aureus. Am. J. Physiol. Lung. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2004;287:L543–L551. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00256.2003. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

