Exploring the Role of Staphylococcus aureus in Inflammatory Diseases
- PMID: 35878202
- PMCID: PMC9318596
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins14070464
Exploring the Role of Staphylococcus aureus in Inflammatory Diseases
Abstract
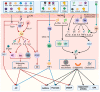
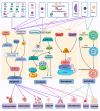
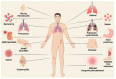
Staphylococcus aureus is a very common Gram-positive bacterium, and S. aureus infections play an extremely important role in a variety of diseases. This paper describes the types of virulence factors involved, the inflammatory cells activated, the process of host cell death, and the associated diseases caused by S. aureus. S. aureus can secrete a variety of enterotoxins and other toxins to trigger inflammatory responses and activate inflammatory cells, such as keratinocytes, helper T cells, innate lymphoid cells, macrophages, dendritic cells, mast cells, neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils. Activated inflammatory cells can express various cytokines and induce an inflammatory response. S. aureus can also induce host cell death through pyroptosis, apoptosis, necroptosis, autophagy, etc. This article discusses S. aureus and MRSA (methicillin-resistant S. aureus) in atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, pulmonary cystic fibrosis, allergic asthma, food poisoning, sarcoidosis, multiple sclerosis, and osteomyelitis. Summarizing the pathogenic mechanism of Staphylococcus aureus provides a basis for the targeted treatment of Staphylococcus aureus infection.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus; apoptosis; autophagy; inflammatory cells; necroptosis; pyroptosis; toxin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Nakagawa S., Matsumoto M., Katayama Y., Oguma R., Wakabayashi S., Nygaard T., Saijo S., Inohara N., Otto M., Matsue H., et al. Staphylococcus aureus Virulent PSMα Peptides Induce Keratinocyte Alarmin Release to Orchestrate IL-17-Dependent Skin Inflammation. Cell Host Microbe. 2017;22:667–677.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2017.10.008. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

