Altered RNome expression in Murine Gastrocnemius Muscle following Exposure to Jararhagin, a Metalloproteinase from Bothrops jararaca Venom
- PMID: 35878210
- PMCID: PMC9321239
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins14070472
Altered RNome expression in Murine Gastrocnemius Muscle following Exposure to Jararhagin, a Metalloproteinase from Bothrops jararaca Venom
Abstract
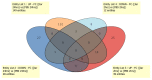
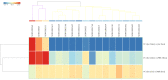
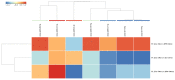
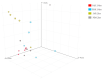
Small RNAs (sRNAs) and microRNAs (miRNAs) are small endogenous noncoding single-stranded RNAs that regulate gene expression in eukaryotes. Experiments in mice and humans have revealed that a typical small RNA can affect the expression of a wide range of genes, implying that small RNAs function as global regulators. Here, we used small RNA deep sequencing to investigate how jararhagin, a metalloproteinase toxin produced from the venom of Bothrops jararaca, affected mmu-miRNAs expression in mice 2 hours (Jar 2hrs) and 24 hours (Jar 24hrs) after injection compared to PBS control. The findings revealed that seven mmu-miRNAs were substantially differentially expressed (p value (p (Corr) cut-off 0.05, fold change ≥ 2) at 2 hrs after jararhagin exposure and that the majority of them were upregulated when compared to PBS. In contrast to these findings, a comparison of Jar 24hrs vs. PBS 24hrs demonstrated that the majority of identified mmu-miRNAs were downregulated. Furthermore, the studies demonstrated that mmu-miRNAs can target the expression of several genes involved in the MAPK signaling pathway. The steady antithetical regulation of mmu-miRNAs may correlate with the expression of genes that trigger apoptosis via MAPK in the early stages, and this effect intensifies with time. The findings expand our understanding of the effects of jararhagin on local tissue lesions at the molecular level.
Keywords: jararhagin; small RNAs; venom.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Jararhagin, a hemorrhagic snake venom metalloproteinase from Bothrops jararaca.Toxicon. 2012 Sep 1;60(3):280-9. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2012.03.026. Epub 2012 Apr 14. Toxicon. 2012. PMID: 22534074 Review.
-
The effect of jararhagin, a metalloproteinase from Bothrops jararaca venom, on pro-inflammatory cytokines released by murine peritoneal adherent cells.Toxicon. 2001 Oct;39(10):1567-73. doi: 10.1016/s0041-0101(01)00131-3. Toxicon. 2001. PMID: 11478964
-
BnP1, a novel P-I metalloproteinase from Bothrops neuwiedi venom: biological effects benchmarking relatively to jararhagin, a P-III SVMP.Toxicon. 2008 Jan;51(1):54-65. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2007.08.005. Epub 2007 Aug 14. Toxicon. 2008. PMID: 17889921
-
Jararhagin and its multiple effects on hemostasis.Toxicon. 2005 Jun 15;45(8):987-96. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2005.02.013. Epub 2005 Apr 2. Toxicon. 2005. PMID: 15922770 Review.
-
Inflammation, angiogenesis and fibrogenesis are differentially modulated by distinct domains of the snake venom metalloproteinase jararhagin.Int J Biol Macromol. 2018 Nov;119:1179-1187. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.08.051. Epub 2018 Aug 11. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018. PMID: 30102981
Cited by
-
Venom biotechnology: casting light on nature's deadliest weapons using synthetic biology.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 May 3;11:1166601. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1166601. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37207126 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ministério-da-Saúde Acidente por Animais Peçonhentos—Descrição da Doença. [(accessed on 28 March 2020)]; Available online: https://www.saude.gov.br/saude-de-a-z/acidentes-por-animais-peconhentos/....
-
- Cardoso J.L., Fan H.W., Franca F.O., Jorge M.T., Leite R.P., Nishioka S.A., Avila A., Sano-Martins I.S., Tomy S.C., Santoro M.L., et al. Randomized comparative trial of three antivenoms in the treatment of envenoming by lance-headed vipers (Bothrops jararaca) in Sao Paulo, Brazil. QJM Int. J. Med. 1993;86:315–325. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

