Improved Therapy of B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma by Obinutuzumab-Dianthin Conjugates in Combination with the Endosomal Escape Enhancer SO1861
- PMID: 35878216
- PMCID: PMC9318199
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins14070478
Improved Therapy of B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma by Obinutuzumab-Dianthin Conjugates in Combination with the Endosomal Escape Enhancer SO1861
Erratum in
-
Correction: Panjideh et al. Improved Therapy of B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma by Obinutuzumab-Dianthin Conjugates in Combination with the Endosomal Escape Enhancer SO1861. Toxins 2022, 14, 478.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Oct 13;14(10):703. doi: 10.3390/toxins14100703. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36287991 Free PMC article.
Abstract
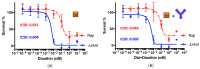
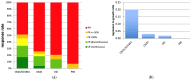
Immunotoxins do not only bind to cancer-specific receptors to mediate the elimination of tumor cells through the innate immune system, but also increase target cytotoxicity by the intrinsic toxin activity. The plant glycoside SO1861 was previously reported to enhance the endolysosomal escape of antibody-toxin conjugates in non-hematopoietic cells, thus increasing their cytotoxicity manifold. Here we tested this technology for the first time in a lymphoma in vivo model. First, the therapeutic CD20 antibody obinutuzumab was chemically conjugated to the ribosome-inactivating protein dianthin. The cytotoxicity of obinutuzumab-dianthin (ObiDi) was evaluated on human B-lymphocyte Burkitt's lymphoma Raji cells and compared to human T-cell leukemia off-target Jurkat cells. When tested in combination with SO1861, the cytotoxicity for target cells was 131-fold greater than for off-target cells. In vivo imaging in a xenograft model of B-cell lymphoma in mice revealed that ObiDi/SO1861 efficiently prevents tumor growth (51.4% response rate) compared to the monotherapy with ObiDi (25.9%) and non-conjugated obinutuzumab (20.7%). The reduction of tumor volume and overall survival was also improved. Taken together, our results substantially contribute to the development of a combination therapy with SO1861 as a platform technology to enhance the efficacy of therapeutic antibody-toxin conjugates in lymphoma and leukemia.
Keywords: anti-CD20; cancer treatment; controlled drug release; dianthin; endocytosis; endosomal escape; glycosylated triterpenoids; immunotoxins; obinutuzumab; targeted toxins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Correction: Panjideh et al. Improved Therapy of B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma by Obinutuzumab-Dianthin Conjugates in Combination with the Endosomal Escape Enhancer SO1861. Toxins 2022, 14, 478.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Oct 13;14(10):703. doi: 10.3390/toxins14100703. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36287991 Free PMC article.
-
Combinatorial approach to increase efficacy of Cetuximab, Panitumumab and Trastuzumab by dianthin conjugation and co-application of SO1861.Biochem Pharmacol. 2015 Oct 1;97(3):247-55. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2015.07.040. Epub 2015 Aug 5. Biochem Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26253687
-
Targeted dianthin is a powerful toxin to treat pancreatic carcinoma when applied in combination with the glycosylated triterpene SO1861.Mol Oncol. 2017 Nov;11(11):1527-1543. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12115. Epub 2017 Sep 15. Mol Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28755527 Free PMC article.
-
Obinutuzumab (GA101) for the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia and other B-cell non-hodgkin's lymphomas: a glycoengineered type II CD20 antibody.Oncol Res Treat. 2015;38(4):185-92. doi: 10.1159/000381524. Epub 2015 Mar 31. Oncol Res Treat. 2015. PMID: 25877943 Review.
-
Combination therapy with the type II anti-CD20 antibody obinutuzumab.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2017 Oct;26(10):1145-1162. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2017.1373087. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2017. PMID: 28845710 Review.
Cited by
-
Synergistic Cytotoxicity of a Toxin Targeting the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor and the Glycosylated Triterpenoid SO1861 in Prostate Cancer.J Cancer. 2023 Sep 18;14(16):3039-3049. doi: 10.7150/jca.85691. eCollection 2023. J Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37859824 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced cytotoxicity of a Pseudomonas Exotoxin A based immunotoxin against prostate cancer by addition of the endosomal escape enhancer SO1861.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jul 6;14:1211824. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1211824. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37484018 Free PMC article.
-
Saponin Fraction CIL1 from Lysimachia ciliata L. Enhances the Effect of a Targeted Toxin on Cancer Cells.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Apr 28;15(5):1350. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15051350. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37242592 Free PMC article.
-
Correction: Panjideh et al. Improved Therapy of B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma by Obinutuzumab-Dianthin Conjugates in Combination with the Endosomal Escape Enhancer SO1861. Toxins 2022, 14, 478.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Oct 13;14(10):703. doi: 10.3390/toxins14100703. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36287991 Free PMC article.
-
Purification of Monoclonal Antibodies Using Chromatographic Methods: Increasing Purity and Recovery.Adv Pharm Bull. 2025 Jan 5;15(1):27-45. doi: 10.34172/apb.43967. eCollection 2025 Apr. Adv Pharm Bull. 2025. PMID: 40636302 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Robak T. GA-101, a third-generation, humanized and glyco-engineered anti-CD20 mAb for the treatment of B-cell lymphoid malignancies. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs. 2009;10:588–596. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

