KSTAR: An algorithm to predict patient-specific kinase activities from phosphoproteomic data
- PMID: 35879309
- PMCID: PMC9314348
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-32017-5
KSTAR: An algorithm to predict patient-specific kinase activities from phosphoproteomic data
Abstract
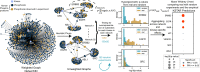
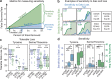
Kinase inhibitors as targeted therapies have played an important role in improving cancer outcomes. However, there are still considerable challenges, such as resistance, non-response, patient stratification, polypharmacology, and identifying combination therapy where understanding a tumor kinase activity profile could be transformative. Here, we develop a graph- and statistics-based algorithm, called KSTAR, to convert phosphoproteomic measurements of cells and tissues into a kinase activity score that is generalizable and useful for clinical pipelines, requiring no quantification of the phosphorylation sites. In this work, we demonstrate that KSTAR reliably captures expected kinase activity differences across different tissues and stimulation contexts, allows for the direct comparison of samples from independent experiments, and is robust across a wide range of dataset sizes. Finally, we apply KSTAR to clinical breast cancer phosphoproteomic data and find that there is potential for kinase activity inference from KSTAR to complement the current clinical diagnosis of HER2 status in breast cancer patients.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Identification of Protein Kinase Drug Targets Using Activity Estimation in Clinical Phosphoproteomics.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2905:163-169. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4418-8_10. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40163304
-
Integrating proteomic and phosphoproteomic data for pathway analysis in breast cancer.BMC Syst Biol. 2018 Dec 21;12(Suppl 8):130. doi: 10.1186/s12918-018-0646-y. BMC Syst Biol. 2018. PMID: 30577793 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphoproteomic analysis reveals PAK2 as a therapeutic target for lapatinib resistance in HER2-positive breast cancer cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Oct 20;505(1):187-193. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.09.086. Epub 2018 Sep 20. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 30243723
-
Insights regarding fungal phosphoproteomic analysis.Fungal Genet Biol. 2017 Jul;104:38-44. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2017.03.003. Epub 2017 Mar 10. Fungal Genet Biol. 2017. PMID: 28288883 Review.
-
Recent Updates on the Therapeutic Potential of HER2 Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors for the Treatment of Breast Cancer.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2018;18(4):306-327. doi: 10.2174/1568009617666170623122213. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2018. PMID: 28669349 Review.
Cited by
-
Systematic analysis of the effects of splicing on the diversity of post-translational modifications in protein isoforms using PTM-POSE.Cell Syst. 2025 Jul 16;16(7):101318. doi: 10.1016/j.cels.2025.101318. Epub 2025 Jun 12. Cell Syst. 2025. PMID: 40513562
-
A computational tool to infer enzyme activity using post-translational modification profiling data.Commun Biol. 2025 Jan 21;8(1):103. doi: 10.1038/s42003-025-07548-4. Commun Biol. 2025. PMID: 39838083 Free PMC article.
-
Inference of differential kinase interaction networks with KINference.Bioinformatics. 2025 Jul 1;41(7):btaf349. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btaf349. Bioinformatics. 2025. PMID: 40579228 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic analysis of the effects of splicing on the diversity of post-translational modifications in protein isoforms using PTM-POSE.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Mar 27:2024.01.10.575062. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.10.575062. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: Cell Syst. 2025 Jul 16;16(7):101318. doi: 10.1016/j.cels.2025.101318. PMID: 38260432 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Network-based elucidation of colon cancer drug resistance mechanisms by phosphoproteomic time-series analysis.Nat Commun. 2024 May 9;15(1):3909. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-47957-3. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38724493 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

