Glycoprotein α-Subunit of Glucosidase II (GIIα) is a novel prognostic biomarker correlated with unfavorable outcome of urothelial carcinoma
- PMID: 35879690
- PMCID: PMC9316353
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-022-09884-8
Glycoprotein α-Subunit of Glucosidase II (GIIα) is a novel prognostic biomarker correlated with unfavorable outcome of urothelial carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Urothelial carcinoma (UC) is among the most prevalent malignancies. The muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC) shows an invasive feature and has poor prognosis, while the non-muscle invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) shows a better prognosis as compared with the MIBC. However, a significant proportion (10%-30%) of NMIBC cases progress to MIBC. Identification of efficient biomarkers for the prediction of the course of UC remains challenging nowadays. Recently, there is an emerging study showed that post-translational modifications (PTMs) by glycosylation is an important process correlated with tumor angiogenesis, invasion and metastasis. Herein, we reported a data-driven discovery and experimental validation of GANAB, a key regulator of glycosylation, as a novel prognostic marker in UC.
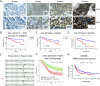
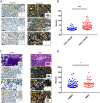
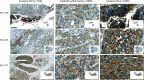
Methods: In the present study, we conducted immunohistochemistry (IHC) assay to evaluate the correlation between the expression levels of GANAB protein and the prognosis of UC in our cohort of 107 samples using whole slide image (WSI) analysis. In vitro experiments using RNAi were also conducted to investigate the biological functions of GANAB in UC cell lines.
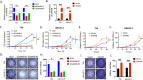
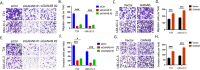
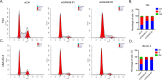
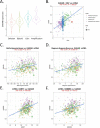
Results: We observed that positive GANAB protein expression was significantly correlated with poor prognosis of UC in our cohort, with p-value of 0.0017 in Log-rank test. Notably, tumor cells at the invasive front of the tumor margin showed stronger GANAB expression than the tumor cells inside the tumor body in UCs. We further validated that the elevated expression levels of GANAB were significantly correlated with high grade tumors (p-values of 1.72 × 10-10), advanced stages (6.47 × 10-6), and elevated in luminal molecular subtypes. Moreover, knocking-down GANAB using RNAi in UM-UC-3 and T24 cells inhibited cell proliferation and migration in vitro. Knockdown of GANAB resulted in cell cycle arrest at G1 phase. We demonstrated that GANAB mediated HIF1A and ATF6 transcriptional activation in the ER stress signaling, and regulated the gene expression of cell cycle-related transcriptional factors E2F7 and FOXM1.
Conclusions: The elevated expression of GANAB is a novel indicator of poorer prognosis of UC. Our data suggests that GANAB is not only a new and promising prognostic biomarker for UC, but also may provide important cues for the development of PTM-based therapeutics for UC treatment.
Keywords: GANAB; Glucosidase; Glycosylation; Post-translational modifications (PTMs); Stress granules (SGs); Urothelial Carcinoma (UC).
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

