Oral dextran sulfate sodium administration induces peripheral spondyloarthritis features in SKG mice accompanied by intestinal bacterial translocation and systemic Th1 and Th17 cell activation
- PMID: 35879738
- PMCID: PMC9310491
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-022-02844-4
Oral dextran sulfate sodium administration induces peripheral spondyloarthritis features in SKG mice accompanied by intestinal bacterial translocation and systemic Th1 and Th17 cell activation
Abstract
Background: Spondyloarthritis (SpA) is an autoimmune and autoinflammatory musculoskeletal disease characterised by systemic enthesitis. Recent research has focused on subclinical inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in SpA pathogenesis. SKG mice, harbouring the Zap70 W163C mutation, increase autoreactive Th17 cells intrinsically, and in a conventional environment, they exhibit spontaneous arthritis with fungal factors. Under SPF conditions, they show SpA features, including enteritis, after peritoneal injection of β-1,3-glucan. This study aimed to clarify whether oral dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) administration, utilised in IBD model mice, can provoke SpA features in SKG mice under SPF conditions, focusing on the relationship between gut microorganisms and SpA pathogenesis.
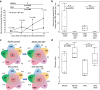
Methods: BALB/c and SKG mice were administered oral DSS, and their body weights, arthritis, and enthesitis scores were recorded. In another cohort, antibiotics (meropenem and vancomycin) or an anti-fungal agent (amphotericin B) was administered orally before DSS administration. The splenic Th1 and Th17 cell populations were examined before and after DSS administration using flow cytometry. Furthermore, the amount of circulating bacterial DNA in whole blood was measured by absolute quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR), and the number and characteristics of bacterial species corresponding to these circulating DNA were analysed by next-generation sequencing (NGS).
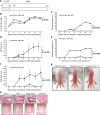
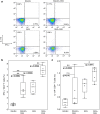
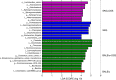
Results: Ankle enthesitis as a peripheral SpA feature was elicited in half of DSS-administered SKG mice, and none of the BALB/c mice. Pre-administration of antibiotics suppressed enthesitis, whilst an anti-fungal agent could not. Th1 and Th17 cell levels in the spleen increased after DSS administration, and this was suppressed by pre-administration of antibiotics. SKG mice have a larger amount of bacterial DNA in whole blood than BALB/c mice before and 1 day after the initiation of DSS administration. The number of bacterial species in whole blood increased after DSS administration in BALB/c and SKG mice. Some genera and species significantly specific to the DSS-treated SKG mouse group were also detected.
Conclusion: Oral DSS administration alone elicited peripheral enthesitis in SKG mice with bacterial translocation accompanied by increased splenic Th1 and Th17 cell levels. Pre-administration of antibiotics ameliorated these DSS-induced SpA features. These findings suggest that intestinal bacterial leakage plays a pivotal role in SpA pathogenesis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interleukin-23 mediates the intestinal response to microbial β-1,3-glucan and the development of spondyloarthritis pathology in SKG mice.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014 Jul;66(7):1755-67. doi: 10.1002/art.38638. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014. PMID: 24664521
-
Rebamipide prevents peripheral arthritis and intestinal inflammation by reciprocally regulating Th17/Treg cell imbalance in mice with curdlan-induced spondyloarthritis.J Transl Med. 2016 Jun 27;14(1):190. doi: 10.1186/s12967-016-0942-5. J Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 27350608 Free PMC article.
-
β-glucan triggers spondylarthritis and Crohn's disease-like ileitis in SKG mice.Arthritis Rheum. 2012 Jul;64(7):2211-22. doi: 10.1002/art.34423. Arthritis Rheum. 2012. PMID: 22328069
-
The SKG model of spondyloarthritis.Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2017 Dec;31(6):895-909. doi: 10.1016/j.berh.2018.07.004. Epub 2018 Aug 7. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 30509448 Review.
-
Gut inflammation and microbiome in spondyloarthritis.Rheumatol Int. 2016 Apr;36(4):457-68. doi: 10.1007/s00296-015-3414-y. Epub 2015 Dec 30. Rheumatol Int. 2016. PMID: 26719306 Review.
Cited by
-
Microbial metabolite drives ageing-related clonal haematopoiesis via ALPK1.Nature. 2025 Jun;642(8066):201-211. doi: 10.1038/s41586-025-08938-8. Epub 2025 Apr 23. Nature. 2025. PMID: 40269158 Free PMC article.
-
Current insights on the roles of gut microbiota in inflammatory bowel disease-associated extra-intestinal manifestations: pathophysiology and therapeutic targets.Gut Microbes. 2023 Dec;15(2):2265028. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2023.2265028. Epub 2023 Oct 11. Gut Microbes. 2023. PMID: 37822139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ankylosing spondylitis and the genetic correlation of extra-articular manifestations: Evidence from bidirectional Mendelian randomization and Bayesian colocalization.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Feb 14;104(7):e41388. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000041388. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 39960913 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroimmune interactions: The bridge between inflammatory bowel disease and the gut microbiota.Clin Transl Med. 2025 May;15(5):e70329. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.70329. Clin Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40400119 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

