Xanthine oxidase inhibitor urate-lowering therapy titration to target decreases serum free fatty acids in gout and suppresses lipolysis by adipocytes
- PMID: 35879786
- PMCID: PMC9310412
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-022-02852-4
Xanthine oxidase inhibitor urate-lowering therapy titration to target decreases serum free fatty acids in gout and suppresses lipolysis by adipocytes
Abstract
Objective: Linked metabolic and cardiovascular comorbidities are prevalent in hyperuricemia and gout. For mechanistic insight into impact on inflammatory processes and cardiometabolic risk factors of xanthine oxidase inhibitor urate-lowering therapy (ULT) titration to target, we performed a prospective study of gout serum metabolomes from a ULT trial.
Methods: Sera of gout patients meeting the 2015 ACR/EULAR gout classification criteria (n = 20) and with hyperuricemia were studied at time zero and weeks 12 and 24 of febuxostat or allopurinol dose titration ULT. Ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectroscopy acquired the serum spectra. Data were assessed using the Metabolon and Metaboloanalyst software. Lipolysis validation assays were done in febuxostat and/or colchicine-treated 3T3-L1 differentiated adipocytes.
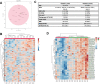
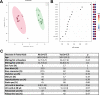
Results: Serum urate decreased from time zero (8.21 ±1.139 SD) at weeks 12 (5.965 ± 1.734 SD) and 24 (5.655 ±1.763 SD). Top metabolites generated by changes in nucleotide and certain amino acid metabolism and polyamine pathways were enriched at 12 and 24 weeks ULT, respectively. Decreases in multiple fatty acid metabolites were observed at 24 weeks, linked with obesity. In cultured adipocytes, febuxostat significantly decreased while colchicine increased the lipolytic response to β-adrenergic-agonism or TNF.
Conclusion: Metabolomic profiles linked xanthine oxidase inhibitor-based ULT titration to target with reduced serum free fatty acids. In vitro validation studies revealed that febuxostat, but not colchicine, reduced lipolysis in cultured adipocytes. Since soluble urate, xanthine oxidase inhibitor treatment, and free fatty acids modulate inflammation, our findings suggest that by suppressing lipolysis, ULT could regulate inflammation in gout and comorbid metabolic and cardiovascular disease.
Keywords: Adipocytes; Gout; Lipolysis; Metabolomics; Microbiome; Xanthine oxidase.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
RT: research grant: Astra-Zeneca; consulting: SOBI, Selecta, Horizon, Allena, Astra-Zeneca
MG: research grant: Pfizer, Novartis
RLB, RC, SMR, BD, HT, DB, KL: none
Figures



References
-
- Johnson RJ, Bakris GL, Borghi C, Chonchol MB, Feldman D, Lanaspa MA, et al. Hyperuricemia, acute and chronic kidney disease, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease: report of a scientific workshop organized by the National Kidney Foundation. Am J Kidney Dis. 2018;71(6):851–865. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2017.12.009. - DOI - PMC - PubMed

