CD8+ T regulatory cells in lupus
- PMID: 35880241
- PMCID: PMC9242525
- DOI: 10.2478/rir-2021-0021
CD8+ T regulatory cells in lupus
Abstract
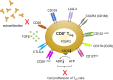
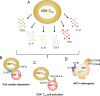
T regulatory cells (Tregs) have a key role in the maintenance of immune homeostasis and the regulation of immune tolerance by preventing the inflammation and suppressing the autoimmune responses. Numerical and functional deficits of these cells have been reported in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients and mouse models of SLE, where their imbalance and dysregulated activities have been reported to significantly influence the disease pathogenesis, progression and outcomes. Most studies in SLE have focused on CD4+ Tregs and it has become clear that a critical role in the control of immune tolerance after the breakdown of self-tolerance is provided by CD8+ Tregs. Here we review the role, cellular and molecular phenotypes, and mechanisms of action of CD8+ Tregs in SLE, including ways to induce these cells for immunotherapeutic modulation in SLE.
Keywords: CD8+ Tregs; anti-DNA Ab; immune homeostasis; immune tolerance; lupus.
© 2021 Ram P. Singh et al., published by Sciendo.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Dr. Hahn has accepted funds for advisory work from Aurinia, GSL, and UCB in the last 12 months. The authors declare that there is no additional financial or commercial conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pathogenesis and novel therapeutics of regulatory T cell subsets and interleukin-2 therapy in systemic lupus erythematosus.Front Immunol. 2023 Sep 12;14:1230264. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1230264. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37771588 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Allogeneic cord blood regulatory T cells decrease dsDNA antibody and improve albuminuria in systemic lupus erythematosus.Front Immunol. 2023 Sep 5;14:1217121. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1217121. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37736101 Free PMC article.
-
The suppression of murine lupus by a tolerogenic peptide involves foxp3-expressing CD8 cells that are required for the optimal induction and function of foxp3-expressing CD4 cells.J Immunol. 2008 Sep 1;181(5):3243-51. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.5.3243. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18713995
-
Targeting Regulatory T Cells to Treat Patients With Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Front Immunol. 2018 Apr 17;9:786. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00786. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29755456 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulatory T Cells in SLE: Biology and Use in Treatment.Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2016 Nov;18(11):67. doi: 10.1007/s11926-016-0616-6. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2016. PMID: 27704250 Review.
Cited by
-
Pathogenesis and novel therapeutics of regulatory T cell subsets and interleukin-2 therapy in systemic lupus erythematosus.Front Immunol. 2023 Sep 12;14:1230264. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1230264. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37771588 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD4+ and CD8+ regulatory T cell characterization in the rat using a unique transgenic Foxp3-EGFP model.BMC Biol. 2023 Jan 12;21(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s12915-022-01502-0. BMC Biol. 2023. PMID: 36635667 Free PMC article.
-
PD-1 activation mitigates lupus nephritis by suppressing hyperactive and heterogeneous PD-1+CD8+ T cells.Theranostics. 2025 Mar 31;15(11):5029-5044. doi: 10.7150/thno.107418. eCollection 2025. Theranostics. 2025. PMID: 40303350 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Crow MK. Collaboration, Genetic Associations, and Lupus Erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:956–961. - PubMed
-
- Hahn BH. Lessons in Lupus: The Mighty Mouse. Lupus. 2001;10:589–593. - PubMed
-
- Filaci G, Bacilieri S, Fravega M. et al. Impairment of CD8+ T Suppressor Cell Function in Patients with Active Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J Immunol. 2001;166:6452–6457. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
