Clinical and histopathological characteristics of COL4A3 c.2881+1G>A variant causing Alport spectrum disorders in Croatian population
- PMID: 35880347
- PMCID: PMC9901899
- DOI: 10.17305/bjbms.2022.7567
Clinical and histopathological characteristics of COL4A3 c.2881+1G>A variant causing Alport spectrum disorders in Croatian population
Abstract
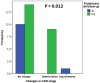
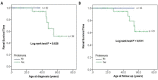
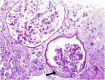
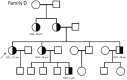
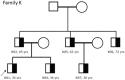
Alport syndrome (AS) and thin basement membrane nephropathy (TBMN) are part of the spectrum of kidney disorders caused by pathogenic variants in α3, α4, or α5 chains of the collagen type IV, the major structural component of the glomerular basement membrane (GBM). Using targeted next-generation sequencing (NGS), 34 AS/TBMN patients (58.8% male) from 12 unrelated families were found positive for heterozygous c.2881+1G>A variant of the COL4A3gene, that is considered disease-causing. All patients were from the continental or island part of Croatia. Clinical, laboratory, and histopathological data collected from the medical records were analyzed and compared to understand the clinical course and prognosis of the affected patients. At the time of biopsy or first clinical evaluation, the mean age was 31 years (median: 35 years; range: 1 - 72 years). Hematuria was present in 33 patients (97.1%) and 19 (55.9%) patients had proteinuria. There were 6 (17.6%) patients with hearing loss, 4 (11.8%) with ocular lesions, and 11 (32.4%) with hypertension. Twenty-three (67.6%) patients had proteinuria at follow-up, and 5 (14.7%) patients with the median age of 48 years (range: 27-55) progressed to kidney failure, started dialysis, or underwent kidney transplantation. Of the 13 patients who underwent kidney biopsy, 4 (30.8%) developed focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS), and 8 (66.7%) showed lamellation of the GBM, including all patients with FSGS. It is essential to conduct a detailed analysis of each collagen type IV genetic variant to optimize the prognosis and therapeutic approach for affected patients.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

