Population-based sequencing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis reveals how current population dynamics are shaped by past epidemics
- PMID: 35880398
- PMCID: PMC9323001
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.76605
Population-based sequencing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis reveals how current population dynamics are shaped by past epidemics
Abstract
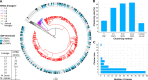
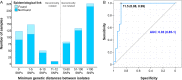
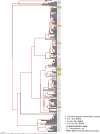
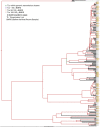
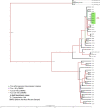
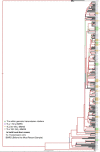
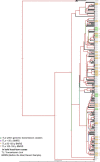
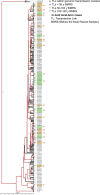
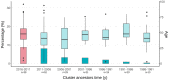
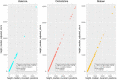
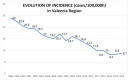
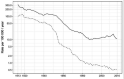
Transmission is a driver of tuberculosis (TB) epidemics in high-burden regions, with assumed negligible impact in low-burden areas. However, we still lack a full characterization of transmission dynamics in settings with similar and different burdens. Genomic epidemiology can greatly help to quantify transmission, but the lack of whole genome sequencing population-based studies has hampered its application. Here, we generate a population-based dataset from Valencia region and compare it with available datasets from different TB-burden settings to reveal transmission dynamics heterogeneity and its public health implications. We sequenced the whole genome of 785 Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains and linked genomes to patient epidemiological data. We use a pairwise distance clustering approach and phylodynamic methods to characterize transmission events over the last 150 years, in different TB-burden regions. Our results underscore significant differences in transmission between low-burden TB settings, i.e., clustering in Valencia region is higher (47.4%) than in Oxfordshire (27%), and similar to a high-burden area as Malawi (49.8%). By modeling times of the transmission links, we observed that settings with high transmission rate are associated with decades of uninterrupted transmission, irrespective of burden. Together, our results reveal that burden and transmission are not necessarily linked due to the role of past epidemics in the ongoing TB incidence, and highlight the need for in-depth characterization of transmission dynamics and specifically tailored TB control strategies.
Keywords: Mycobacterium tuberculosis; epidemiology; genomic epidemiology; global health; transmission; tuberculosis; whole-genome sequencing.
© 2022, Cancino-Muñoz, López et al.
Conflict of interest statement
IC, ML, MT, LV, RB, MB, MB, JC, EC, JC, IE, OE, FG, AG, CG, AG, BG, DG, NG, MG, JL, CM, RM, DN, MN, NO, EP, JP, JR, MR, HV, IC No competing interests declared, CC Reviewing editor, eLife, IC received consultancy fees from Foundation for innovative new diagnostics. The author has no other competing interests to declare
Figures

References
-
- Auld SC, Shah NS, Mathema B, Brown TS, Ismail N, Omar SV, Brust JCM, Nelson KN, Allana S, Campbell A, Mlisana K, Moodley P, Gandhi NR. Extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis in South Africa: genomic evidence supporting transmission in communities. The European Respiratory Journal. 2018;52:1800246. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00246-2018. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Belda-Álvarez M. ThePipeline. swh:1:rev:a725827cb664e6d995823f3f30fcd1d7e16f63d2Software Heritage. 2022 https://archive.softwareheritage.org/swh:1:dir:115b2aef41f207f8a43e56791...
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

