Evaluation of the Aptima HBV Quant Assay Compared to Abbott RealTime M2000 HBV Quant Assay and Procleix Ultrio Plus dHBV Assay in Plasma Samples
- PMID: 35880868
- PMCID: PMC9431630
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.01761-22
Evaluation of the Aptima HBV Quant Assay Compared to Abbott RealTime M2000 HBV Quant Assay and Procleix Ultrio Plus dHBV Assay in Plasma Samples
Abstract
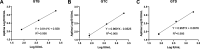
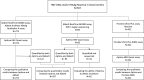
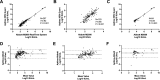
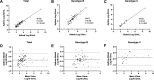
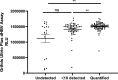
Analytical performance of hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA quantitative assay is critical for screening infection and initiating and monitoring antiviral treatment. In this study, the limit of detection (LoD) and linearity of Aptima HBV Quant assay were evaluated, and analytical performance was compared with that of the Abbott RealTime M2000 HBV Quant assay and the Procleix Ultrio Plus dHBV assay in plasma samples. The LoDs for genotypes B, C, and D plasma samples were 2.139 (1.531, 4.520), 3.120 (2.140, 7.373), and 3.330 (2.589, 4.907) IU/mL, respectively. The R2 value fitted by linear regression of serially diluted samples less than 2,000 IU/mL was above 0.9. There was no difference in positive rate between Aptima and Abbott or between Aptima and Procleix. Quantitative results of Aptima and Abbott showed good correlation with an r of >0.9 using Spearman analysis, while the quantitative results of Aptima were slightly lower than those of Abbott. Usual mutations in the HBV S region had no impact on Aptima assay. This study showed that Aptima is a dual-targeted transcription-mediated amplification (TMA) assay suitable for HBV DNA detection in clinical practice, with quantitative performance comparable to that of the Abbott RealTime M2000 HBV Quant assay and qualitative performance comparable to that of the Procleix Ultrio Plus dHBV assay. IMPORTANCE The Aptima HBV Quant assay (Hologic Inc., San Diego, CA, USA) is a dual-target real-time transcription-mediated amplification (RT-TMA) assay. This study aims to evaluate whether this assay is suitable for HBV DNA detection. As a result, the assay showed high sensitivity with LoDs below 3.5 IU/mL. The amplification efficiency of Aptima for samples below 2,000 IU/mL is adequate for clinical practice, with an R2 of >0.9 fitted by linear regression. Usual mutations in the HBV S region did not affect the performance of Aptima. Moreover, its performance was comparable to the widely used Abbott RealTime M2000 HBV Quant assay for detecting HBV DNA in plasma specimens. Although not indicated for use as a diagnostic or blood screening assay, the Aptima HBV Quant assay demonstrated comparable qualitative performance to the Procleix Ultrio Plus dHBV system.
Keywords: Abbott RealTime M2000 HBV Quant assay; Aptima HBV Quant assay; HBV DNA; Procleix Ultrio Plus dHBV assay; dual-target; limit of detection; mutation; real-time TMA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Letter to the Editor: Performance Analysis of the Aptima HBV Quant Assay for Hepatitis B virus DNA Quantification in Plasma.Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2022 Jul;52(4):684-685. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2022. PMID: 36197782
-
Analytical characteristics and comparative evaluation of Aptima HCV quant Dx assay with the Abbott RealTime HCV assay and Roche COBAS AmpliPrep/COBAS TaqMan HCV quantitative test v2.0.Virol J. 2017 Apr 4;14(1):66. doi: 10.1186/s12985-017-0727-3. Virol J. 2017. PMID: 28372576 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the aptima HIV-1 quant Dx, HCV quant Dx and HBV quant assays against the Abbott HIV-1, HCV and HBV RealTime assays.J Clin Virol. 2018 Sep;106:7-10. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2018.06.015. Epub 2018 Jun 25. J Clin Virol. 2018. PMID: 30007139
-
The New Aptima HBV Quant Real-Time TMA Assay Accurately Quantifies Hepatitis B Virus DNA from Genotypes A to F.J Clin Microbiol. 2017 Apr;55(4):1211-1219. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02219-16. Epub 2017 Feb 15. J Clin Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28202793 Free PMC article.
-
Performance evaluation of the Aptima® HCV Quant Dx assay for hepatitis C virus (HCV) RNA detection and quantification in comparison to the Abbott RealTime HCV assay.J Clin Virol. 2017 Jul;92:1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2017.04.013. Epub 2017 Apr 26. J Clin Virol. 2017. PMID: 28475925
References
-
- World Health Organization. 2017. Global hepatitis report. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland.
-
- World Health Organization. 2018. Hepatitis B. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland. https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-b.
-
- Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Society of Hepatology. 2019. The guidelines of prevention and treatment for chronic hepatitis B (2019 version). Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi 27:938–961. (In Chinese.) - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

