Inhibition of Biofilm Formation and Virulence Factors of Cariogenic Oral Pathogen Streptococcus mutans by Shikimic Acid
- PMID: 35880891
- PMCID: PMC9431622
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.01199-22
Inhibition of Biofilm Formation and Virulence Factors of Cariogenic Oral Pathogen Streptococcus mutans by Shikimic Acid
Abstract
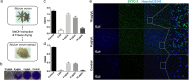
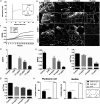
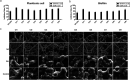
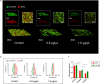
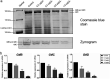
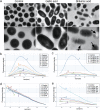
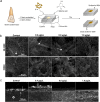
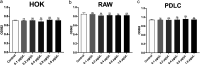
Streptococcus mutans is known as an important oral pathogen causing dental caries, a widespread oral infectious disease. S. mutans synthesize exopolysaccharide (EPS) using glucosyltransferases (Gtfs), resulting in biofilm formation on the tooth surface. Bacterial cells in the biofilms become strongly resistant to a harsh environment, such as antibiotics and host defense mechanisms, making biofilm-based infections difficult to eliminate. Discovering novel antibiofilm agents, especially from natural products, helps to develop effective strategies against this kind of diseases. The present study investigated the inhibitory effect of shikimic acid (SA), one abundant compound derived from Illicium verum extract, on the biofilm formation of S. mutans. We found SA can reduce the EPS synthesized by this oral pathogen and modulate the transcription of biofilm formation related genes, leading to fewer bacterial cells in its biofilm. SA also interacted with cell membrane and membrane proteins, causing damage to bacterial cells. Ex vivo testing of biofilm formation on bovine teeth showed SA strongly decreased the number of S. mutans cells and the number of EPS accumulated on dental enamel surfaces. Moreover, SA exhibits almost no toxicity to human oral cells evaluated by in vitro biocompatibility assay. In conclusion, shikimic acid exhibits remarkable antibiofilm activity against S. mutans and has the potential to be further developed as a novel anticaries agent. IMPORTANCE Natural products are an important and cost-effective source for screening antimicrobial agents. Here, we identified one compound, shikimic acid, from Illicium verum extract, exhibiting antimicrobial activity against S. mutans proliferation. It also inhibits biofilm formation of this bacteria through decreasing Gtf expression and EPS synthesis. Furthermore, this compound exhibits no significant cytotoxicity at its MIC against S. mutans, providing evidence for its clinical application.
Keywords: anti-biofilm agent; dental biofilm; glucosyltransferase; natural compound; shikimic acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

