SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination elicits robust antibody responses in children
- PMID: 35881018
- PMCID: PMC9348753
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abn9237
SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination elicits robust antibody responses in children
Abstract
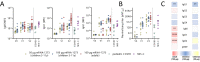
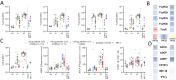
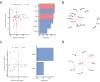
Although children have been largely spared from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), the emergence of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) variants of concern (VOCs) with increased transmissibility, combined with fluctuating mask mandates and school reopenings, has led to increased infections and disease among children. Thus, there is an urgent need to roll out COVID-19 vaccines to children of all ages. However, whether children respond equivalently to adults to mRNA vaccines and whether dosing will elicit optimal immunity remain unclear. Here, we aimed to deeply profile the vaccine-induced humoral immune response in 6- to 11-year-old children receiving either a pediatric (50 μg) or adult (100 μg) dose of the mRNA-1273 vaccine and to compare these responses to vaccinated adults, infected children, and children who experienced multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C). Children elicited an IgG-dominant vaccine-induced immune response, surpassing adults at a matched 100-μg dose but more variable immunity at a 50-μg dose. Irrespective of titer, children generated antibodies with enhanced Fc receptor binding capacity. Moreover, like adults, children generated cross-VOC humoral immunity, marked by a decline of omicron-specific receptor binding domain, but robustly preserved omicron spike protein binding. Fc receptor binding capabilities were also preserved in a dose-dependent manner. These data indicate that both the 50- and 100-μg doses of mRNA vaccination in children elicit robust cross-VOC antibody responses and that 100-μg doses in children result in highly preserved omicron-specific functional humoral immunity.
Figures

References
-
- Siegel D. A., Reses H. E., Cool A. J., Shapiro C. N., Hsu J., Boehmer T. K., Cornwell C. R., Gray E. B., Henley S. J., Lochner K., Suthar A. B., Lyons B. C., Mattocks L., Hartnett K., Adjemian J., van Santen K. L., Sheppard M., Soetebier K. A., Logan P., Martin M., Idubor O., Natarajan P., Sircar K., Oyegun E., Dalton J., Perrine C. G., Peacock G., Schweitzer B., Morris S. B., Raizes E.; MAPW1 , Trends in COVID-19 Cases, Emergency Department Visits, and Hospital Admissions Among Children and Adolescents Aged 0-17 Years - United States, August 2020-August 2021. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 70, 1249–1254 (2021). 10.15585/mmwr.mm7036e1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- CDC.gov, Center For Disease Control And Prevention.
-
- Delahoy M. J., Ujamaa D., Whitaker M., O’Halloran A., Anglin O., Burns E., Cummings C., Holstein R., Kambhampati A. K., Milucky J., Patel K., Pham H., Taylor C. A., Chai S. J., Reingold A., Alden N. B., Kawasaki B., Meek J., Yousey-Hindes K., Anderson E. J., Openo K. P., Teno K., Weigel A., Kim S., Leegwater L., Bye E., Como-Sabetti K., Ropp S., Rudin D., Muse A., Spina N., Bennett N. M., Popham K., Billing L. M., Shiltz E., Sutton M., Thomas A., Schaffner W., Talbot H. K., Crossland M. T., McCaffrey K., Hall A. J., Fry A. M., McMorrow M., Reed C., Garg S., Havers F. P.; COVID-NET Surveillance Team; COVID-NET Surveillance Team , Hospitalizations Associated with COVID-19 Among Children and Adolescents - COVID-NET, 14 States, March 1, 2020-August 14, 2021. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 70, 1255–1260 (2021). 10.15585/mmwr.mm7036e2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

