Intraoperative radiotherapy during awake craniotomies: preliminary results of a single-center case series
- PMID: 35881316
- PMCID: PMC9663365
- DOI: 10.1007/s10143-022-01838-9
Intraoperative radiotherapy during awake craniotomies: preliminary results of a single-center case series
Abstract
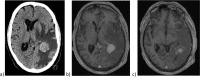
Awake craniotomies are performed to avoid postoperative neurological deficits when resecting lesions in the eloquent cortex, especially the speech area. Intraoperative radiotherapy (IORT) has recently focused on optimizing the oncological treatment of primary malignant brain tumors and metastases. Herein, for the first time, we present preliminary results of IORT in the setting of awake craniotomies. From 2021 to 2022, all patients undergoing awake craniotomies for tumor resection combined with IORT were analyzed retrospectively. Demographical and clinical data, operative procedure, and treatment-related complications were evaluated. Five patients were identified (age (mean ± standard deviation (SD): 65 ± 13.5 years (y)). A solid left frontal metastasis was detected in the first patient (female, 49 y). The second patient (male, 72 y) presented with a solid metastasis on the left parietal lobe. The third patient (male, 52 y) was diagnosed with a left temporoparietal metastasis. Patient four (male, 74 y) was diagnosed with a high-grade glioma on the left frontal lobe. A metastasis on the left temporooccipital lobe was detected in the fifth patient (male, 78 y). After awake craniotomy and macroscopic complete tumor resection, intraoperative tumor bed irradiation was carried out with 50 kV x-rays and a total of 20 Gy for 16.7 ± 2.5 min. During a mean follow-up of 6.3 ± 2.6 months, none of the patients developed any surgery- or IORT-related complications or disabling permanent neurological deficits. Intraoperative radiotherapy in combination with awake craniotomy seems to be feasible and safe.
Keywords: Awake craniotomy; Eloquently located brain tumor; Intraoperative radiotherapy; Preliminary results.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Bilger A, Bretzinger E, Fennell J, Nieder C, Lorenz H, Oehlke O, Grosu AL, Specht HM, Combs SE. Local control and possibility of tailored salvage after hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy of the cavity after brain metastases resection. Cancer Med. 2018;7(6):2350–2359. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1486. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cifarelli CP, Brehmer S, Vargo JA, Hack JD, Kahl KH, Sarria-Vargas G, Giordano FA. Intraoperative radiotherapy (IORT) for surgically resected brain metastases: outcome analysis of an international cooperative study. J Neurooncol. 2019;145(2):391–397. doi: 10.1007/s11060-019-03309-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Esenou C, Rincon-Torroella J, ReFaey K, Lee YM, Nangiana J, Vivas-Buitrago T, Quinones-Hinojosa A. Awake craniotomy vs craniotomy under general anesthesia for perirolandic gliomas: evaluating perioperative complications and extent of resection. Neurosurgery. 2017;81(3):481–489. doi: 10.1093/neuros/nyx023. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

