The e-mental health treatment in Stockholm myocardial infarction with non-obstructive coronaries or Takotsubo syndrome study (E-SMINC): a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 35883115
- PMCID: PMC9315084
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-022-06530-3
The e-mental health treatment in Stockholm myocardial infarction with non-obstructive coronaries or Takotsubo syndrome study (E-SMINC): a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial
Abstract
Background: In the aftermath of a myocardial infarction with non-obstructive coronary arteries (MINOCA) or Takotsubo syndrome (TS), patients commonly express high levels of stress and anxiety. Current treatment alternatives rarely address these issues.
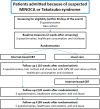
Methods: The study is a randomised controlled trial, where 90 patients with a discharge diagnosis of MINOCA or TS who also report symptoms of stress or anxiety will be randomised 2-6 weeks after their cardiac event. The treatment consists of 10 weeks of Internet-based cognitive behaviour therapy (CBT) and starts immediately after randomisation for the treatment group. The control group receives usual care. Main outcomes are symptoms of anxiety measured with the Hospital Anxiety and Depression scale, anxiety subscale, and perceived stress measured with the Perceived Stress Scale, 14-item version, 10 weeks after randomisation. Secondary measures include cardiac specific anxiety, symptoms of post-traumatic stress, quality of life, cortisol measured in hair and physiological stress responses (heart rate variability, blood pressure and saliva cortisol) during a stress procedure. Ten weeks after randomisation, the control group will also receive treatment. Long-term follow-up in the self-report measures mentioned above will be conducted 20 and 50 weeks after randomisation where the total group's development over time is followed, and the groups receiving intervention early versus late compared.
Discussion: At present, there are no randomised studies evaluating psychological treatment for patients with MINOCA or TS. There is an urgent need for treatment alternatives aiming at relieving stress and anxiety considering the high mental stress and anxiety levels observed in MINOCA and TS, leading to decreased quality of life. CBT aiming at reducing mental stress has been shown to be effective regarding prognosis in patients with coronary artery disease. The current protocol describes a randomised open-label controlled trial evaluating an Internet-based CBT program for reduction of stress and anxiety in patients with increased mental stress and/or anxiety with a discharge diagnosis of either MINOCA or TS.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT04178434 . Registered on 26 November 2019.
Keywords: Anxiety; Cognitive behavioural therapy; Internet-based intervention; MINOCA; Randomised controlled trial; Stress; Takotsubo syndrome.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests. LK is a voluntary patient research partner who is a member of the patient organisation The Swedish Heart and Lung Association. Her participation is not in any way related to the funding to the present study from that organisation.
References
-
- Agewall S, Beltrame JF, Reynolds HR, Niessner A, Rosano G, Caforio ALP, et al. ESC working group position paper on myocardial infarction with non-obstructive coronary arteries [Internet]. Eur Heart J. 2017:143–53 Available from: https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article-lookup/doi/10.1093/eurheartj/.... - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tamis-Holland JE, Jneid H, Reynolds HR, Agewall S, Brilakis ES, Brown TM, et al. Contemporary diagnosis and management of patients with myocardial infarction in the absence of obstructive coronary artery disease: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2019;139. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical