Teachers' characteristics predict students' guidance for healthy lifestyle: a cross-sectional study in Arab-speaking schools
- PMID: 35883162
- PMCID: PMC9321300
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-022-13795-5
Teachers' characteristics predict students' guidance for healthy lifestyle: a cross-sectional study in Arab-speaking schools
Erratum in
-
Correction: Teachers' characteristics predict students' guidance for healthy lifestyle: a cross-sectional study in Arab-speaking schools.BMC Public Health. 2022 Aug 17;22(1):1553. doi: 10.1186/s12889-022-13902-6. BMC Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35974332 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Introduction: Schools are valuable settings for implementing healthy lifestyle interventions. Teachers' health behaviors affect their health and well-being and might affect their position as role models for students. This study aimed a) to assess health behaviors, health perceptions, burnout, job satisfaction, and organizational commitment among Arab school teachers in Israel; b) to examine the relationship between these variables; and c) to explain the variance of healthy lifestyle promotion among students.
Methods: A cross-sectional study using a structured questionnaire was conducted among 150 teachers (mean age 39 years, 85% women) in May-June 2020.
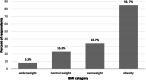
Results: Most respondents (79%) were overweight and obese, 79% reported unhealthy nutrition and not reaching the recommended physical activity target, 47% slept >7 hours at night and 54% defined their health status as very good or excellent. Reported burnout levels were high. Organizational commitment and job satisfaction were high while students' guidance towards a healthy lifestyle was moderate. Burnout was negatively correlated with health perception, organizational commitment, and job satisfaction. Health perception was positively correlated with organizational commitment, job satisfaction and promoting a healthy lifestyle among students. Logistic regression analysis revealed that job satisfaction, performance of PA according to the recommendations and burnout predicted 51% of the variance of healthy lifestyle promotion among students.
Conclusions: Teachers in Israeli Arab schools report unfavorable health behaviors and health perception as well as high burnout levels. The findings suggest implementing intervention programs to reduce teacher burnout and creating organizational conditions that would encourage teachers to adopt a healthy lifestyle and help them promote healthy lifestyle habits among their students.
Keywords: Burnout; Health behaviors; Job satisfaction student guidance; Organizational commitment; Teacher.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- He L, Zhai Y, Engelgau M, Li W, Qian H, Si X, et al. Association of children's eating behaviors with parental education, and teachers' health awareness, attitudes and behaviors: a national school-based survey in China. Eur J Public Health. 2014;24:880–887. doi: 10.1093/eurpub/ckt177. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Inchley J, et al. Adolescent Obesity and Related Behaviours: Trends and Inequalities in the WHO European Region, 2002-2014. Observations from the Health Behaviour in School-Aged Children (HBSC) WHO Collaborative Cross-National Study. Copenhagen: World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe; 2007.
-
- Robbins SP, Coulter M. Management. 7th ed. Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall; 2003.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources