Usefulness of the Measurement of Serum Paraoxonase-1 Arylesterase Activity in the Diagnoses of COVID-19
- PMID: 35883435
- PMCID: PMC9312761
- DOI: 10.3390/biom12070879
Usefulness of the Measurement of Serum Paraoxonase-1 Arylesterase Activity in the Diagnoses of COVID-19
Abstract
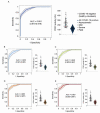
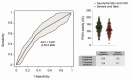
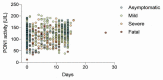
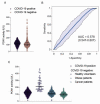
The development of inexpensive, fast, and reliable screening tests for COVID-19 is, as yet, an unmet need. The present study was aimed at evaluating the usefulness of serum arylesterase activity of paraoxonase-1 (PON1) measurement as a screening test in patients with different severity levels of COVID-19 infection. We included 615 COVID-19-positive patients who were classified as asymptomatic, mildly symptomatic, severely symptomatic, or fatally symptomatic. Results were compared with 50 healthy volunteers, 330 patients with cancer, and 343 with morbid obesity. Results showed PON1 activity greatly decreased in COVID-19 compared to healthy volunteers; a receiver operating characteristics plot showed a high diagnostic accuracy. The degree of COVID-19 severity did not influence PON1 levels. Our results indicated that PON1 determination was efficient for disease diagnosis, but not for prognosis. Furthermore, patients with obesity or cancer presented alterations similar to those of COVID-19 patients. As such, elevated levels of PON1 indicate the absence of COVID-19, but low levels may be present in various other chronic diseases. The assay is fast and inexpensive. We suggest that PON1 measurement could be used as an initial, high cut-off point screening method, while lower values should be confirmed with the more expensive nucleic acid amplification test.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; biomarkers; paraoxonase-1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funder had no role in the study design, data collection, analysis, decision to publish, or manuscript preparation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association between inflammatory markers and serum paraoxonase and arylesterase activities in the general population: a cross-sectional study.Lipids Health Dis. 2021 Jul 31;20(1):81. doi: 10.1186/s12944-021-01508-7. Lipids Health Dis. 2021. PMID: 34332593 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased serum paraoxonase and arylesterase activities in patients with rosacea.J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015 Feb;29(2):367-370. doi: 10.1111/jdv.12556. Epub 2014 May 22. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015. PMID: 24854673
-
Association between alcohol consumption and serum paraoxonase and arylesterase activities: a cross-sectional study within the Bavarian population.Br J Nutr. 2016 Feb 28;115(4):730-6. doi: 10.1017/S0007114515004985. Epub 2016 Jan 15. Br J Nutr. 2016. PMID: 26769660
-
Paraoxonase-1 (PON1) activity as a risk factor for atherosclerosis in chronic renal failure patients.Hemodial Int. 2008 Oct;12(4):471-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1542-4758.2008.00311.x. Hemodial Int. 2008. PMID: 19090870
-
Levels of paraoxonase and arylesterase activities and malondialdehyde in workers exposed to ionizing radiation.Cell Biochem Funct. 2003 Dec;21(4):371-5. doi: 10.1002/cbf.1042. Cell Biochem Funct. 2003. PMID: 14624476
Cited by
-
Diagnostic accuracy of artificial intelligence-based multi-spectrum analysis for molecular fingerprint detection of SARS-CoV-2.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 May 23;104(21):e41928. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000041928. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40419915 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic Reprogramming in Respiratory Viral Infections: A Focus on SARS-CoV-2, Influenza, and Respiratory Syncytial Virus.Biomolecules. 2025 Jul 16;15(7):1027. doi: 10.3390/biom15071027. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40723899 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum Levels of Arachidonic Acid, Interleukin-6, and C-Reactive Protein as Potential Indicators of Pulmonary Viral Infections: Comparative Analysis of Influenza A, Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection, and COVID-19.Viruses. 2024 Jul 1;16(7):1065. doi: 10.3390/v16071065. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39066228 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma Proteomics Elucidated a Protein Signature in COVID-19 Patients with Comorbidities and Early-Diagnosis Biomarkers.Biomedicines. 2024 Apr 10;12(4):840. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12040840. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38672194 Free PMC article.
-
Modulatory Effect of Lifestyle-Related, Environmental and Genetic Factors on Paraoxonase-1 Activity: A Review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Feb 5;20(4):2813. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20042813. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36833509 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rodríguez-Tomàs E., Iftimie S., Castañé H., Baiges-Gaya G., Hernández-Aguilera A., González-Viñas M., Castro A., Camps J., Joven J. Clinical performance of paraoxonase-1-related variables and novel markers of inflammation in coronavirus disease-19. A machine learning approach. Antioxidants. 2021;10:991. doi: 10.3390/antiox10060991. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gobierno de España. Ministerio de Sanidad Recomendaciones de Seguridad del Paciente y Profesionales en Procedimientos Intervencionistas en la Fase de Transición de la Pandemia COVID-19. [(accessed on 20 May 2022)]; Available online: https://www.sanidad.gob.es/gl/profesionales/saludPublica/ccayes/alertasA....
-
- NIH COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines. Clinical Spectrum of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. [(accessed on 20 May 2022)]; Available online: https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/overview/clinical-spectrum/
-
- Fort-Gallifa I., García-Heredia A., Hernández-Aguilera A., Simó J.M., Sepúlveda J., Martín-Paredero V., Camps J., Joven J. Biochemical indices of oxidative stress and inflammation in the evaluation of peripheral artery disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016;97:568–576. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.07.011. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

