MicroRNAs at the Crossroad between Immunoediting and Oncogenic Drivers in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 35883486
- PMCID: PMC9313100
- DOI: 10.3390/biom12070930
MicroRNAs at the Crossroad between Immunoediting and Oncogenic Drivers in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
Treatments aimed to reverse the tumor-induced immune tolerance represent a promising approach for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Notwithstanding, primary nonresponse, early, and late disease reactivation still represent major clinical challenges. Here, we focused on microRNAs (miRNAs) acting both as modulators of cancer cell hallmarks and immune system response. We outlined the bidirectional function that some oncogenic miRNAs play in the differentiation and program activation of the immune system development and, at the same time, in the progression of HCC. Indeed, the multifaceted spectrum of miRNA targets allows the modulation of both immune-associated factors and oncogenic or tumor suppressor drivers at the same time. Understanding the molecular changes contributing to disease onset, progression, and resistance to treatments might help to identify possible novel biomarkers for selecting patient subgroups, and to design combined tailored treatments to potentiate antitumor approaches. Preliminary findings seem to argue in favor of a bidirectional function of some miRNAs, which enact an effective modulation of molecular pathways driving oncogenic and immune-skipping phenotypes associated with cancer aggressiveness. The identification of these miRNAs and the characterization of their 'dual' role might help to unravel novel biomarkers identifying those patients more likely to respond to immune checkpoint inhibitors and to identify possible therapeutic targets with both antitumor and immunomodulatory functions. In the present review, we will focus on the restricted panel of miRNAs playing a bidirectional role in HCC, influencing oncogenic and immune-related pathways at once. Even though this field is still poorly investigated in HCC, it might represent a source of candidate molecules acting as both biomarkers and therapeutic targets in the setting of immune-based treatments.
Keywords: HCC; biomarkers; immune system; microRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
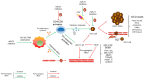
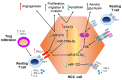
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

