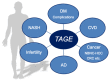
Effects of Toxic AGEs (TAGE) on Human Health
- PMID: 35883620
- PMCID: PMC9317028
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11142178
Effects of Toxic AGEs (TAGE) on Human Health
Abstract
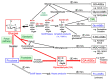
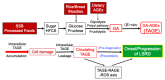
The habitual and excessive consumption of sugar (i.e., sucrose and high-fructose corn syrup, HFCS) is associated with the onset and progression of lifestyle-related diseases (LSRD). Advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) have recently been the focus of research on the factors contributing to LSRD. Approaches that inhibit the effects of AGEs may be used to prevent and/or treat LSRD; however, since the structures of AGEs vary depending on the type of reducing sugars or carbonyl compounds to which they respond, difficulties are associated with verifying that AGEs are an etiological factor. Cytotoxic AGEs derived from glyceraldehyde, a triose intermediate in the metabolism of glucose and fructose, have been implicated in LSRD and are called toxic AGEs (TAGE). A dietary imbalance (the habitual and excessive intake of sucrose, HFCS, or dietary AGEs) promotes the generation/accumulation of TAGE in vivo. Elevated circulating levels of TAGE have been detected in non-diabetics and diabetics, indicating a strong relationship between the generation/accumulation of TAGE in vivo and the onset and progression of LSRD. We herein outline current findings on "TAGE as a new target" for human health.
Keywords: advanced glycation end-products (AGEs); healthy life expectancy; human health; lifestyle-related diseases (LSRD); toxic AGEs (TAGE).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no conflict of interest exist.
Figures
References
-
- Imamura F., O’Connor L., Ye Z., Mursu J., Hayashino Y., Bhupathiraju S.N., Forouhi N.G. Consumption of sugar sweetened beverages, artificially sweetened beverages, and fruit juice and incidence of type 2 diabetes: Systematic review, meta-analysis, and estimation of population attributable fraction. Br. J. Sports Med. 2016;50:496–504. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2016-h3576rep. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schwingshackl L., Hoffmann G., Lampousi A.M., Knüppel S., Iqbal K., Schwedhelm C., Bechthold A., Schlesinger S., Boeing H. Food groups and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2017;32:363–375. doi: 10.1007/s10654-017-0246-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

