Integrin Signaling Shaping BTK-Inhibitor Resistance
- PMID: 35883678
- PMCID: PMC9322986
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11142235
Integrin Signaling Shaping BTK-Inhibitor Resistance
Abstract
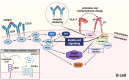
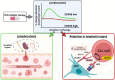
Integrins are adhesion molecules that function as anchors in retaining tumor cells in supportive tissues and facilitating metastasis. Beta1 integrins are known to contribute to cell adhesion-mediated drug resistance in cancer. Very late antigen-4 (VLA-4), a CD49d/CD29 heterodimer, is a beta1 integrin implicated in therapy resistance in both solid tumors and haematological malignancies such as chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). A complex inside-out signaling mechanism activates VLA-4, which might include several therapeutic targets for CLL. Treatment regimens for this disease have recently shifted towards novel agents targeting BCR signaling. Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) is a component of B cell receptor signaling and BTK inhibitors such as ibrutinib are highly successful; however, their limitations include indefinite drug administration, the development of therapy resistance, and toxicities. VLA-4 might be activated independently of BTK, resulting in an ongoing interaction of CD49d-expressing leukemic cells with their surrounding tissue, which may reduce the success of therapy with BTK inhibitors and increases the need for alternative therapies. In this context, we discuss the inside-out signaling cascade culminating in VLA-4 activation, consider the advantages and disadvantages of BTK inhibitors in CLL and elucidate the mechanisms behind cell adhesion-mediated drug resistance.
Keywords: BTK; CD49d; CLL; VLA-4; acalabrutinib; animal models; ibrutinib; pirtobrutinib; therapy resistance; zanubrutinib.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

