Efficacy of a Tibia Counter Rotator System for the Treatment of Internal Tibial Torsion in Children
- PMID: 35883954
- PMCID: PMC9322744
- DOI: 10.3390/children9070970
Efficacy of a Tibia Counter Rotator System for the Treatment of Internal Tibial Torsion in Children
Abstract
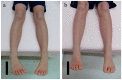
Internal tibial torsion is more common in the Asian population than in Western populations. Generally, surgery should be considered for the treatment of severe internal tibial torsion. As an alternative approach, the usefulness of a tibia counter rotator (TCR), a corrective orthosis based on the theory of the tibia torsional transformer, has been demonstrated, but the evidence is limited. In the present study, the efficacy and safety of TCR treatment were investigated in pediatric patients with internal tibial torsion. The subjects were 124 pediatric patients with internal tibial torsion who were between 3 and 15 years of age and had no underlying diseases. The severity of tibial intorsion was evaluated by the tibial transmalleolar angle (TMA). A TMA less than 5° was defined as internal tibial torsion, and less than −20° was defined as severe in this study. The median duration of TCR use was 11 (9, 12) (median (IQR: interquartile range)) months, and the treatment completion rate was 94.4% (117/124). The TMA at 12 months from the start of treatment in patients who completed treatment was 5° (0°, 10°) on the right (n = 66) (p < 0.01 vs. pretreatment) and 0° (−5°, 8°) on the left (n = 71) (p < 0.01 vs. pretreatment). The tibial torsional transformer used in this study is effective in the initial treatment of mild to severe internal tibial torsion, with no adverse effects. Although internal tibial torsion is generally expected to resolve spontaneously, TCR treatment may be an effective alternative to surgical therapy in the Asian pediatric population.
Keywords: in-toeing gait; knee joint diseases; toe-out gait plate; transmalleolar angle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The therapeutic effect of tibia counter rotator with toe-out gait plate in the treatment of tibial internal torsion in children.Ann Rehabil Med. 2014 Apr;38(2):218-25. doi: 10.5535/arm.2014.38.2.218. Epub 2014 Apr 29. Ann Rehabil Med. 2014. PMID: 24855616 Free PMC article.
-
In-toeing gait in children with clubfoot and the effect of tibial rotation osteotomy.J Pediatr Orthop B. 2020 Jul;29(4):348-354. doi: 10.1097/BPB.0000000000000688. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2020. PMID: 31651746
-
Distal tibial rotation osteotomies normalize frontal plane knee moments.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010 Dec 1;92(17):2835-42. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.J.00147. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010. PMID: 21123614
-
Common rotational variations in children.J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2003 Sep-Oct;11(5):312-20. doi: 10.5435/00124635-200309000-00004. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2003. PMID: 14565753 Review.
-
[Torsion and torsional development of the lower extremities].Orthopade. 2019 Jun;48(6):523-530. doi: 10.1007/s00132-019-03752-3. Orthopade. 2019. PMID: 31089774 Review. German.
Cited by
-
An Evaluation of Orthotics on In-Toeing or Out-Toeing Gait.Healthcare (Basel). 2025 Feb 28;13(5):531. doi: 10.3390/healthcare13050531. Healthcare (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40077093 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decision Tree-Based Foot Orthosis Prescription for Patients with Pes Planus.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Sep 30;19(19):12484. doi: 10.3390/ijerph191912484. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36231782 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

