Molecular Characterization of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Isolated from Intensive Care Unit Patients in Jordanian Hospitals
- PMID: 35884089
- PMCID: PMC9311868
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics11070835
Molecular Characterization of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Isolated from Intensive Care Unit Patients in Jordanian Hospitals
Abstract
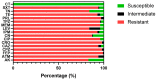
Acinetobacter baumannii is a common cause of healthcare-associated infections (HAI) worldwide, mostly occurring in intensive care units (ICUs). Extended-spectrum beta lactamases (ESBL)-positive A. baumannii strains have emerged as highly resistant to most currently used antimicrobial agents, including carbapenems. The most common mechanism for carbapenem resistance in this species is β-lactamase-mediated resistance. Carbapenem-hydrolyzing class D oxacillinases are widespread among multidrug-resistant (MDR) A. baumannii strains. The present study was conducted to determine the presence and distribution of blaOXA genes among multidrug-resistant A. baumannii isolated from ICU patients and genes encoding insertion sequence (IS-1) in these isolates. Additionally, the plasmid DNA profiles of these isolates were determined. A total of 120 clinical isolates of A. baumannii from various ICU clinical specimens of four main Jordanian hospitals were collected. Bacterial isolate identification was confirmed by biochemical testing and antibiotic sensitivity was then assessed. PCR amplification and automated sequencing were carried out to detect the presence of blaOXA-51, blaOXA-23, blaOXA-24, and blaOXA-58 genes, and ISAba1 insertion sequence. Out of the 120 A. baumannii isolates, 95% of the isolates were resistant to three or more classes of the antibiotics tested and were identified as MDR. The most frequent resistance of the isolates was against piperacillin (96.7%), cephalosporins (97.5%), and β-lactam/β-lactamase inhibitor combinations antibiotics (95.8%). There were 24 (20%) ESBL-producing isolates. A co-existence of blaOXA-51 gene and ISAba1 in all the 24 ESBL-producing isolates was determined. In addition, in the 24 ESBL-producing isolates, 21 (87.5%) carried blaOXA-51 and blaOXA-23 genes, 1 (4.2%) carried blaOXA-51 and blaOXA-24, but all were negative for the blaOXA-58 gene. Plasmid DNA profile A and profile B were the most common (29%) in ESBL-positive MDR A. baumannii isolates while plasmid DNA profile A was the most common in the ESBL-negative isolates. In conclusion, there was an increase in prevalence of MDR-A. baumannii in ICU wards in Jordanian hospitals, especially those having an ESBL phenotype. Thus, identification of ESBL genes is necessary for the surveillance of their transmission in hospitals.
Keywords: Acinetobacter baumannii; ESBL; ICU; Jordan; Oxa carbapenems; insertion sequence; multidrug resistance genes; plasmid DNA profile.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Alsulaiman D., Al-Hamed N., Alziadi A., Almalaihi A., Alessa M., Khalil R., Joseph R., Alshayban D. Evaluation of acinetobacter baumannii pneumonia among critically ill patients in a tertiary care hospital in Saudi Arabia. Heliyon. 2020;6:e03976. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e03976. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

