Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in the Hypoxic Tumor Microenvironment
- PMID: 35884382
- PMCID: PMC9320406
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14143321
Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in the Hypoxic Tumor Microenvironment
Abstract
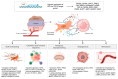
Solid cancers are composed of malignant cells and their surrounding matrix components. Hypoxia plays a critical role in shaping the tumor microenvironment that contributes to cancer progression and treatment failure. Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) are one of the most prominent components of the tumor microenvironment. CAFs are highly sensitive to hypoxia and participates in the crosstalk with cancer cells. Hypoxic CAFs modulate several mechanisms that induce cancer malignancy, such as extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling, immune evasion, metabolic reprogramming, angiogenesis, metastasis, and drug resistance. Key signaling molecules regulating CAFs in hypoxia include transforming growth factor (TGF-β) and hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs). In this article, we summarize the mechanisms underlying the hypoxic regulation of CAFs and how hypoxic CAFs affect cancer development and progression. We also discuss the potential therapeutic strategies focused on targeting CAFs in the hypoxic tumor microenvironment.
Keywords: cancer; cancer-associated fibroblast; hypoxia; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


References
-
- Sahai E., Astsaturov I., Cukierman E., DeNardo D.G., Egeblad M., Evans R.M., Fearon D., Greten F.R., Hingorani S.R., Hunter T., et al. A framework for advancing our understanding of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2020;20:174–186. doi: 10.1038/s41568-019-0238-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

