Effects of Exosomal Viral Components on the Tumor Microenvironment
- PMID: 35884611
- PMCID: PMC9317196
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14143552
Effects of Exosomal Viral Components on the Tumor Microenvironment
Abstract
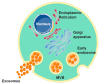
Exosomes are extracellular membrane vesicles with a diameter of 30-100 nm, produced by different eukaryotic cells that contain multitudinous lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins. They transfer membrane components and nucleic acids between cells, thereby performing an information exchange between cells. Many studies have shown that a variety of tumor-associated viruses can exert their biological functions through exosomes. The tumor microenvironment (TME) is very important in the occurrence, development, and chemoresistance of tumors. It is composed of tumor cells, fibroblasts, endothelial cells, immune cells, stromal cells, and acellular components, such as exosomes and cytokines. This review focuses on the effects of virus-related components secreted by tumor cells over the TME in several virus-associated cancers.
Keywords: cancers; exosome; oncovirus; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

